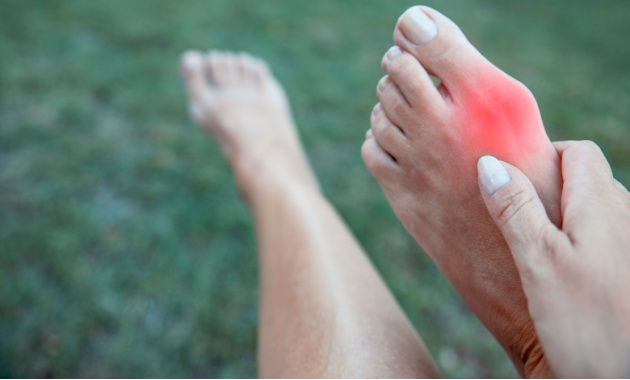
A bunion is a painful bony knot-like structure that develops inside of the foot. It is caused as a result of constant pressure on the feet which compresses the big toe. It pushes the big toe towards the second toe. Over a period of time, an extra bone grows at the point of junction of the big toe and foot.
Bunions develop gradually and are clearly visible as the big toe joint leans towards the second toe. The condition worsens over time and the person finds it difficult to wear shoes or walk. Bunions are more common in women and most of the people who develop dead skin under the toes have a positive family history. It is estimated that approximately 70% of the patients have a large genetic component [1]. It is found in at least 2% of children aged 9 to 10 years [2].
Buy the support aid for your ankle, foot, and leg.
Most bunions develop due to repetitive injury to the foot from wearing shoes with a heel and narrow toe box. The other possible causes are:
Research suggests that arthritic conditions increase the risk of developing bunions. This is because in some cases RA causes your body to mistakenly attack the lining of your big toe joint that triggers bunion.
The symptoms of RA and bunion are identical including swelling and loss of mobility in the affected joint.
Looking for supplements for joint bone, joint, and muscle care? Buy Now!
Connective tissue disorders
Connective tissues are the structures that hold the body together. These tissues are made up of several proteins, collagen, and elastin. They are found in several connective organs of the skin and joints. The disorders that cause the inflammation of these tissues increase the risk of developing bunions.This is because inflammation may weaken the support of the joint which predisposes the individual to develop bunions. The connective tissue disorders that can cause bunion are Marfan syndrome, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, and Down syndrome.
Muscle imbalance
There are several layers of the muscles in the foot. These layers are very important for the smooth movement of the joint. The first and third layer of the foot called intrinsic layers hold the bones of the foot together and give it its shape. The second layer of the muscle is very strong and helps in the movement.
The increased forefoot pressure over a prolonged period of time causes muscle imbalance of the foot. Moreover, certain medical conditions such as stroke and cerebral palsy can also lead to muscle imbalance. These conditions can cause bunions to develop. This is because of the limited range of motion of the big toes that causes the development of bony protrusions.
Lifestyle intervention
Bunions usually develop as a result of repeated stress on the foot from outside of the big toe. This type of shoe can trigger the development of bunions. People who wear the following type of shoes are more prone to bunions:
-Tight shoes
-Heels
-Poorly fitted shoes
-Shoes with a narrow and pointed-toe box
Women have 10 times more chances of developing bunions due to the use of heels [4]. Moreover, people in occupations that involve a lot of standing and walking are more susceptible to bunions. Such professions include:
-Teaching
-Nursing
-Ballet dancers
-Athletes
Tips to manage bunions
The pain of the bunions can be managed through several lifestyle changes. These include:
-Avoid wearing heels and pointed shoes
-Avoid long walks
-Use the right mix of hot and cold therapy
-Indulge in specific exercises such as toe curls and marble pick-ups
-Maintain a healthy weight
Conclusion
Bunions are the deformity of the big toe which causes it to bend towards the other toe. The symptoms include pain, limitation in walking, and problems with wearing normal shoes. The exact cause is not well understood. However, it tends to occur more often in women and people who wear tight shoes or heels. The treatment options include non-surgical approaches such as the use of wider shoes, avoiding heels, and maintaining a healthy weight.
If this is ineffective, surgical management is recommended. Patients typically tolerate the surgery well and can return to work approximately 6 to 12 weeks post-surgery. Improvement has shown to occur as far out as one year post-surgery.
(The article is written by Kanchan Vats, Team Lead, and reviewed by Monalisa Deka, Senior Health Content Editor)
References
1. Ferrari Jill, Bunions [Updated 2009]. BMJ Clinical Evidence. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2907787/
2. Kuhn James and Alvi Farhan, Hallux Valgus [Updated September 29 2022]. Stat Pearls. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK553092/
3. T.D Marloes, V.D.L Marike, P.M Thea, Dekker Loost, Multidisciplinary recommendations for diagnosis and treatment of foot problems in people with rheumatoid arthritis [Updated 2018]. Journal Of Foot and Ankle Research. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6030746/
4. Cologne Germany, Bunions [Updated 2021].Institute for Quality and Efficiency in Health Care (IQWiG). Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513134/