10th-16th March is World Glaucoma Week. The aim of the week is to raise awareness about glaucoma and motivate people to have regular eye checkups to eliminate blindness caused due to glaucoma.
Glaucoma is one of the leading cause of blindness in the world. According to a 2014 study[1], glaucoma affects more than 70 million people worldwide. In 2015, there were 57.5 million people worldwide with primary open-angle glaucoma, a type of glaucoma, and it was expected to increase to 65.5 million people by 2020[2]. In India, glaucoma is the leading cause of irreversible blindness with at least 12 million people affected and nearly 1.2 million people blind from the disease[3]. Hence, this world glaucoma week, let’s learn a bit about what is glaucoma, the risk factors and symptoms of glaucoma and when to go to an ophthalmologist.
What Is Glaucoma?
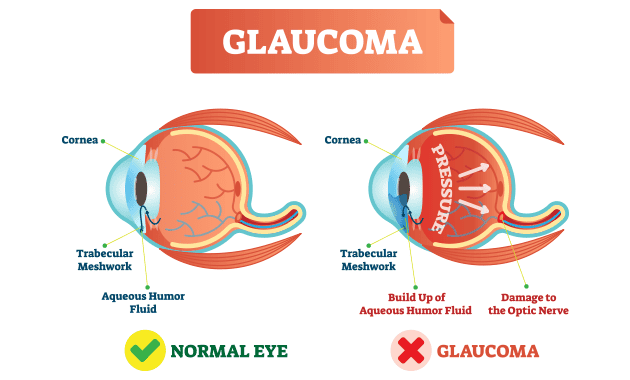
Glaucoma is a set of progressive optic nerve condition that can lead to severe vision problems and blindness.
The eye produces a fluid known as aqueous humour which keeps the eye moist. This fluid leaves the eye through openings in the cornea and iris. However, any damage or blockage of these openings can increase the pressure in the eye, which is known as intraocular pressure. This increase in the eye pressure can damage the optic nerve, which in turn can affect the vision, even leading to blindness.
The exact cause of an increase in eye pressure is not known. But it is believed that several factors can increase the pressure in the eyes which include
-High blood pressure
-Diabetes
-Poor blood flow to the optic nerve
-Medications such as corticosteroids
-Blocked drainage in the eyes
-Use of dilating eye drops
Don’t Be Blind To The Risks Of Bad Eyesight..!! Opt For Affordable Eye Care Products Today.
What Are The Signs And Symptoms Of Glaucoma?
Many patients with glaucoma are asymptomatic and do not know they have the disease. More than 90 per cent of these cases remain undiagnosed due to the lack of symptoms of glaucoma. However, there are certain signs and symptoms of glaucoma that should not be ignored. These include:
Halos around light: When the pressure in the rises quickly due to closed angle glaucoma, the cornea becomes waterlogged which can affect the vision leading to halos around lights.
Pain in the eyes: It is mostly seen when there is a sudden buildup of pressure. It does not act as one of the characteristic features/symptoms of glaucoma when the rise in pressure is gradual and not sudden.
Tunnel vision: It is one of the common symptoms of glaucoma. In this, the pressure on the nerves can damage the retinal nerve fibres which can lead to a characteristic pattern of vision loss. This leads to tunnel vision in which the peripheral vision is blocked. For example, when seeing a photo, you may not be able to see the peripheral picture but can see the centre portion of the picture with clarity. This can be seen when undergoing testing of the eyes.
Changes in the optic disc: The rise in intraocular pressure can lead to cupped, pale optic disc which acts as the key symptoms of glaucoma.
Enlargement of the eye: In kids below three years of age, enlargement of the eye due to raised intraocular pressure can occur. It is one of the characteristic symptoms of glaucoma. In adults, the eye cannot enlarge greatly because growth has ceased.
(The article is reviewed by Dr. Lalit Kanodia, General Physician)
Recommended Reads:
Stop Blaming Your Computer Screen For Watery Eyes. Here’s Why!
Types Of Eye Specialists: Ophthalmologist, Optician and Optometrist
References:
1. Weinreb RN, Aung T, Medeiros FA. The pathophysiology and treatment of glaucoma: a review. JAMA. 2014 May 14;311(18):1901-11.
2. Foris LA, Tripathy K. Open Angle Glaucoma. In: StatPearls. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2018 Jan.
3. World Glaucoma Week. The National Health Portal India.