Do you sneeze often or get an itch from certain fabrics like wool? Do you have to think twice when you go out to eat, as you end up with an unpleasant reaction? If yes, you can be suffering from what is known as allergy. According to the Asthma and Allergy Foundation of America, almost 30% adults and 40% children are allergic to certain substances at some time in their life.
What is an allergy?
Allergy is a hypersensitivity condition where an individual’s immune system overreacts to innocuous substances in the environment, which otherwise won’t affect most of the individuals.
The immune system of the body plays a protective role and fights against pathogenic substances like bacteria and viruses. In normal individuals, the immune system produces antibodies, which are molecules that fight the pathogen. In allergic individuals, the immune system wrongly detects a harmless substance (allergen) as a pathogenic one and produces an antibody against it. These antibodies remain in the system even after the substance is eliminated from the body. This causes the body to recognize the allergen on subsequent exposure and launch an attack against it. This process is known as sensitization.
Know your allergy triggers

Various substances can trigger an allergic reaction; these are known as allergens. Allergens can be indoor or environmental. An individual can be allergic to one or multiple substances. Some of the common allergens are as follows:
1.Dust
2.Latex
3.Pollens
4.Drugs
5.Cockroaches and animal dander
6.Food items like peanuts, fish, eggs, and wheat
7.Mould
Here is a list of some commonly caused allergies
1)Skin allergies
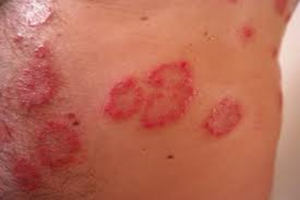

As the skin is the largest organ, it is more commonly seen to be affected by allergens. Some of the common skin allergies are as follows:
| Condition | Description | Common allergens | Symptoms |
| Urticaria (Hives) |
Exposure to allergens causes the release of chemicals like histamine, which affects the blood vessels underneath the skin and causes them to leak, resulting in rash formation. Only superficial layers of the skin are affected. | a) Food b) Certain medications c) Insects or parasites |
Red, itchy, and raised welts on the skin
|
| Angioedema | It is similar to urticaria, the difference being the involvement of deeper skin layers. | a) Food b) Certain medications c) Insects or parasites |
1) Painful swelling of eyelids, lips, and inside of the throat 2) Faintness, dizziness, and breathlessness |
| Eczema
(Atopic dermatitis) |
Inflammation of the skin after exposure to the allergen. The cause is genetic in most of the cases. | a) Chemicals b) Perfumes c) Pets d) Fabrics |
1) Dry and itchy patches of skin 2) Small blisters on skin that ooze and develops crust |
| Allergic contact dermatitis | Irritation and inflammation of the skin after direct contact with the allergen | a) Cosmetics b) Deodorants c) Bleach d) Soap and hand sanitizer |
1) Blisters filled with clear fluid 2) Redness, itching, and swelling |
2)Respiratory allergies
Both upper and lower respiratory tracts can be affected by allergy.
| Condition | Description | Allergens | Symptoms |
| Allergic rhinitis | Swelling and irritation of the mucous membrane of the nose | 1) Pollen 2) Dander |
Sneezing, watering of nose, nasal itching, stuffy nose, and headache |
| Allergic sinusitis | Inflammation of the soft tissues lining the sinuses, which are air-filled cavity surrounding nasal cavity | 1) Pollen 2) Dust Mites 3) Pet Dander |
Headache, running nose, facial pain, and nasal congestion |
| Allergic asthma | Allergens get in the respiratory system, resulting in inflammation and contraction of the airways. | 1) Pollen 2) Animal Fur 3) Dust mite 4) Perfumes |
Coughing, wheezing, shortness of breath, and tightness in chest |
3)Food allergies


A food allergy occurs when the immune system overreacts to a food item or a substance in it. It is most commonly genetic and affects 6-8% of children under the age of 3 years and 3% adults. Food allergy can be IgE-mediated, non-IgE-mediated, and mixed reaction.
IgE-mediated allergies: They occur due to the production of food-specific IgE antibodies. The symptoms occur within 1-2 hours of ingesting the food item. Some of the common conditions are as follows:
| System involved | Common conditions | Symptoms | Common food items |
| Skin | 1) Acute urticaria and angioedema 2) Atopic dermatitis |
1) Redness, itching, and swelling of skin 2) Dryness of skin and small blisters that ooze and forms crust. |
Milk, fish, vegetables, fruits |
| Gastrointestinal tract | Oral Allergy Syndrome (type of contact urticaria that is limited to lips or throat) | Painful swelling of lips and inside of the throat | Raw fruit and vegetables like pear, peach, carrot, and apple |
| Respiratory | 1) Allergic rhinitis 2) Allergic asthma |
1) Running nose, sneezing, and headache 2) Breathlessness, faintness, and coughing |
Milk, eggs, peanuts, tree nut, and shellfish |
| Anaphylaxis | Breathlessness, hives, lightheadedness, and vomiting | Milk, eggs, peanuts, tree nut, and shellfish |
Non-IgE-mediated allergies:
It is a cell-mediated reaction, mainly T cell-mediated, which is a type of white blood cell. The symptoms occur hours or even a day after ingestion of the food item. Some of the common conditions are as mentioned below:
| System involved | Common conditions | Symptoms/ Presentation | Common food items |
| Skin | 1) Atopic dermatitis 2) Dermatitis herpetiformis |
1) Itching, dryness, and blisters 2) Itching rash on extensor surfaces like elbow, knees, and buttocks |
Gluten |
| Gastrointestinal tract | 1) Food protein-induced enterocolitis(inflammation of the intestine) syndrome 2) Eosinophilic oesophagitis 3) Celiac disease |
1) Diarrhea and vomiting 2) Difficulty swallowing and regurgitation of food3) Fat in stool, chronic diarrhea, and weight loss |
Multiple foods like milk, eggs, and peanuts |
| Respiratory | Pulmonary hemosiderosis | Iron deficiency anemia and recurrent pneumonia | Eggs and milk |
Mixed or both IgE- and cell-mediated allergies:
As the name suggests, the reaction is due to the activation of both IgE and cell-mediated responses to a specific food item. Some of the common examples include eosinophilic gastroenteritis and eosinophilic esophagitis.
4)Dust Allergy

It is the commonest cause of indoor allergies, where dust mites in the household dust result in an allergic reaction.
Dust mites are microscopic creatures and measure about one quarter or one-third of a millimeter. Dust mites thrive on skin cells shed by humans, pet dander, and fiber of pillows or bed sheets. They are commonly found in a warm (68-770F) and humid environment.
Some of the common symptoms include:
●Sneezing
●Watering of the eyes
●Itchy skin
●Watering of the nose and eyes
●Stuffed nose
5)Eye allergy

Commonly known as ocular allergy or allergic conjunctivitis, is a condition where the delicate membrane covering the eye (conjunctiva) is allergic to specific substances. Though allergic conjunctivitis can happen during any month of a year, it is more commonly observed in summer, spring, and winter season.
| Common conditions | Symptoms | Common triggers |
| 1) Allergic conjunctivitis
2) Vernal keratoconjunctivitis(more severe form of conjunctivitis and more commonly seen in young boys) 3) Giant papillary conjunctivitis(associated with contact lenses) |
1) Itching, redness, and burning of eyes. Thin and watery discharge from the eyes.
2) Itching, pricking sensation, and thick discharge from the eyes. 3) Itching, puffiness, and blurred vision.
|
a) Indoor allergens like dust mite and pet dander b) Outdoor allergens like pollen, grass, trees, and weed. c) Irritants like perfume, diesel exhaust, and cigarette smoke. |
6)Drug allergies

An allergic reaction to a specific drug is not common and seen in only 5 to 10% of the cases. This should not be confused with the side effects of the drug. Side effects can be seen in any individual, and it doesn’t involve the immune system. On the other hand, a drug allergy is seen only in specific people and is a reaction of the immune system.
Some of the common triggers of drug allergies are as follows:
●Sulfa drugs
●Penicillin and related antibiotics
●Drugs used for chemotherapy
●Anticonvulsants
●Ibuprofen, aspirin, and other non-steroidal anti- inflammatory drugs (NSAIDS)
Some of the common symptoms are as follows:
●Minor drug allergy can cause hives, rash, and itching.
●Other symptoms include nausea, vomiting, abdominal cramps, dizziness, and seizures.
●More serious reactions result in breathlessness and swelling of lips and tongue and can also cause death.
7)Mold allergy
Molds are fungi whose spores spread through air, especially during dry windy weather. These allergies are more common during the rainy season as they require a damp environment to grow. Some of the molds that cause allergies are Fusarium, Cladosporium, Aspergillus, and Alternaria.
Loggers, farmers, carpenters, mill workers, and bakers are at a higher risk of developing mold allergy. People with mold allergy experience the following symptoms:
●Breathing difficulty
●Hives
●Itching and swelling of eyes
8)Insect sting allergy

Warm weather brings with it insects that sting such as yellow jackets, bees, fire ants, and wasps. A common reaction to most of the sting is redness, swelling, and itching of the affected part. An allergic reaction occurs only when the immune system overreacts to the insect sting. Allergic reaction to a sting bite occurs within minutes but it can also be delayed up to 24 hours. The common presentation of insect allergy is as follows:
●Swelling of the face, throat, or tongue
●Stomach cramps
●Dizziness
●Diarrhea or nausea
Severe reaction to the venom of an insect can also result in an anaphylactic reaction.
9)Pet allergy

An allergic reaction to the protein in pet’s dander, skin, urine, and saliva is common. Though pet allergy can be seen to any animal with fur, it is commonly associated with cats and dogs. Some of the common symptoms of pet allergy are as follows:
●Nasal congestion
●Red and itchy eyes
●Sneezing
●Running of nose
●Post nasal drip
10) Latex allergy

It is an allergic reaction to proteins present in rubber. Latex or natural rubber is procured from the sap of Hevea brasiliensis tree. Reaction to latex can be an immediate allergic reaction or delayed (allergic contact dermatitis). The immediate reaction is very severe and commonly presents as painful swelling of the lips, tongue, or inside of the throat. It can also result in an anaphylactic reaction.
Allergic contact dermatitis, on another hand, results in a reaction that typically occurs after 12-48 hours of exposure to latex. It manifests itself as dry, itchy, and scaly skin.
Tests to detect your allergies

Skin prick test: A liquid containing the substance which you might be allergic to is introduced on the skin and the area is gently pricked with a needle. A red bump will develop within 15 minutes in case of allergy to that substance.
Intradermal skin test: In this test, a small amount of allergen is injected in the outer layer of the skin and is done in case of a negative skin prick test. It is most commonly performed for venom or food allergy.
Blood test: Blood is collected and checked for specific antibodies in response to an allergen.
Elimination diet: It involves avoiding a specific food item to check for improvement and starting it again to check for reaction.
Patch test: Here a small amount of allergen is placed on the skin and covered with a bandage. In case of contact dermatitis, a patch is visible after 48-96 hours.
Managing allergies
Avoidance
An effective way to fight an allergy is avoiding the allergen that causes it. This can sound obvious, but it is easier said than done. It can be simpler avoiding a food item, but ubiquitous allergens like dust can be difficult to completely avoid.
In case of allergy to dust mites, maintaining a bed hygiene is a crucial step. You can avoid dust mite by encasing your pillow, mattress, and bed sheet with dust mite proof encasing. These should also be washed with hot water and special detergent that can kill dust mites.
Medication
Some of the commonly used medications are decongestants, antihistamines, and corticosteroids.
●Decongestants are used to relieve symptoms like stuffy nose. They help drain nasal passages and thus relieve the discomfort. Though useful, they should not be used for a prolonged duration, as can cause rebound effect (increase in symptoms after a medicine is discontinued, mostly due to drug dependence).
●Antihistamines can block the effect of histamine, which is commonly released during an allergic reaction. Common antihistamines are fexofenadine, cetirizine, diphenhydramine , etc. Some of them have side effects and hence should not be taken without consulting a doctor.
●Corticosteroids are used to control itching and swelling.
Immune therapy
This is the last resort and helps alleviate an allergy over an extended period. Intervention includes injection shots that reduce antibodies that launch an immune attack, thus altering the body’s defense against them.
It’s not easy to live a life where harmless substances can prove a threat to life. However, it is important to identify your triggers and avoid them. Next time you have any of the above-mentioned symptoms, try to understand the type of allergy and the trigger behind it. Take the help of an expert can who will help to diagnose the condition. Most allergies are easier to treat once the exact cause is determined.
1,152 total views, 2 views today