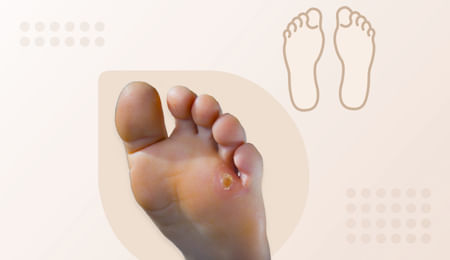
Corns
Corns are calloused areas of skin that develop to protect skin from damage against prolonged rubbing, pressure, and other forms of irritation. Calluses and corns typically form on the hands or feet.
Corns and calluses can be caused by many factors, such as wearing too fitted or too loose shoes, not wearing socks, walking barefoot regularly, etc. Other risk factors may include joint problems or other foot-related problems like bunions or hammer toe. These conditions can be prevented by reducing or removing the causes which lead to increased pressure at specific points on the hands or feet.
Corns and calluses can be treated with medicated products which chemically break down the thickened, dead skin. Salicylic acid is usually the main ingredient used in most corn and callus removal products.
People with fragile skin, poor circulation in the feet (due to conditions such as diabetes or peripheral arterial disease), and repeated formation of corns should consult a podiatrist or a healthcare professional for the appropriate management of this condition.
- Adults
- Both men and women
- Feet and hands
- Plantar wart
- Poroma
- Warty dyskeratoma
- Calcinosis cutis
- Gout and pseudogout
- Hypertrophic lichen planus
- Interdigital neuroma
- Lichen simplex chronicus
- Palmoplantar keratoderma
- Keratosis punctata of palmar creases
- Porokeratosis plantaris discreta
- Porokeratosis palmoplantar et disseminata
- Dermoscopy
- Radiographs
- Pressure studies
- Topical keratolytic agents
- Laser therapy
- Surgery
- Podiatrist
- Dermatologist
- General physician
- General surgeon
- Orthopedic
Symptoms Of Corns
The following signs and symptoms may indicate corns:
-
Flesh-colored dry, hard, rough papules with a whitish center (called the core), usually located over a bony prominence
-
A raised hardened bump in which the center may be a dense knot of skin
-
Can cause pain when walking
-
A thick, rough area of skin
-
Tenderness or pain under the skin
-
Flaky, dry, or waxy skin
Corns can be of the following types:
-
Hard corns: They are usually small and occur on the bony areas of feet and hands.
-
Soft corns: They are whitish in color, have a rubbery texture, and may look like an open sore which might be painful. They usually occur between the toes and in moist and sweaty skin areas.
A callus is a section of skin that thickens because of friction, pressure, or irritation. It often happens on the feet but can also occur on the hands, elbows, or knees. However, corns and calluses are not the same things.
-
Calluses are usually asymptomatic, but if friction is extreme, they may thicken and cause irritation and mild burning discomfort.
-
Callus is less circumscribed than corn, is usually larger, does not have a central core, and may or may not be painful.
Causes Of Corns
The bones of the feet have many projections. Excessive pressure is applied to the skin overlying these bony projections either by poorly fitted shoes or some kind of foot deformity, such as hammer toes.
The body tries to protect this irritated skin by accumulating the outermost layer of the epidermis. But this accumulation causes a prominence that further increases the pressure on bony projections, leading to a vicious cycle and eventually the formation of corns and calluses.
Risk Factors For Corns
Here are some intrinsic and extrinsic risk factors that can lead to the development of corns and calluses:
Extrinsic (outside) factors
-
Poorly fitted or open footwear
-
Irregularities in the shoes, such as a poorly positioned seam or stitching
-
High heels
-
Wearing shoes without socks
-
Physical activities that lead to excessive pressure and friction, including running, jogging, climbing, etc.
-
Professions that cause repeated friction or pressure on skin, e.g., athletes or construction workers
Intrinsic (from within) factors
-
Bony prominences
-
Malunion fracture
-
Faulty foot mechanics
-
Cavovarus foot (a foot with an arch higher than normal, and that turns in at the heel)
-
Toe deformity (Claw, hammer, mallet)
-
Short first metatarsal (the shortest of the metatarsal bones located at the base of the big toe)
-
Hallux rigidus (stiff big toe)
-
Transfer lesion from osteotomy or removal of adjacent metatarsal head
-
Overweight
Diagnosis Of Corns
In most cases, doctors can diagnose corns and calluses by visual examination. However, other diagnostic methods include:
Medical history and physical examination
The doctor will inspect the feet for certain signs and symptoms of corns along with following at the initial stages:
-
Patients footwear and information about any previous treatments like osteotomies, orthoses etc.
-
Patient’s gait and alignment of feet for faulty mechanics
-
Location and characteristic of keratotic lesions
-
Problems with the structure of foot bones
-
Bone alignment
Imaging tests
The doctor may perform the following imaging tests to conclude the reason for corn formation:
-
Dermoscopy: It is a noninvasive technique primarily used to examine skin lesions and areas affected by hyperkeratosis.
-
Radiographs: X-rays of weight-bearing feet may help show any bony prominences that contribute to corn formation.
Other tests
Some other tests used by healthcare professionals to investigate the underlying cause of corns and calluses are:
-
Blood tests: Tests such as fasting glucose level and rheumatoid factors are done to find the etiology of foot deformities in some patients.
-
Pedobarographic studies: Pressure studies (pedobarographs) of the feet can highlight areas of excessive pressure associated with corns.
Prevention Of Corns
Following are some tips to prevent corns and calluses:
-
Wear properly fitted shoes. The shoes should neither be forcibly broken into nor should be too loose. Instead they should be comfortable to wear right out of the box.
-
Allow a space of 1/2 inch between the end of the shoe and the longest toe. For athletic shoes, allow up to 1 inch.
-
Check the width of the shoes. Adequate room should be allowed across the ball of the foot. The first metatarsophalangeal joint should be in the widest part of the shoe.
-
The heel should fit snugly.
-
Check the fit over the instep. A shoe with laces allows for adjustment of this area.
-
Avoid activities that apply repeated friction or pressure to the skin.
-
Wear gloves and properly fitted socks with no irritating stitching.
Suffering from cracked heels? Read about how to heal cracked heels naturally.
Specialist To Visit
Corns are not life-threatening, but can cause a lot of trouble and irritation if left untreated. Doctors who can help diagnose and treat corns include:
-
Podiatrist
-
Dermatologist
-
General physician
-
General surgeon
-
Orthopedic
When to visit a doctor?
If you observe that corns and calluses are causing pain and discomfort or affecting your daily life in any way, you are advised to see a podiatrist, a foot specialist.
Remember: People with certain comorbidities, like diabetes, poor circulation, or any other serious illness, should have their feet checked from time to time.
If you notice any symptoms of corns or calluses, seek medical advice.
Feel free to consult our stellar professionals from the comfort of your home.
Treatment Of Corns
Corns and calluses can become a hinderance in daily life activities and may require treatment for a better quality of life.
The principles of treatment should be:
-
To provide symptomatic relief
-
To determine mechanical etiology
-
To formulate a conservative plan by advising on footwear and prescribing orthoses
-
To consider surgery if conservative measures fail.
The following treatment protocols may be considered for the management of corns:
-
Manual removal: Use a nail file, emery board, or pumice stone immediately after bathing to manually remove hyperkeratotic tissue.
-
Topical keratolytic agents: These agents facilitate lesion pairing by softening the corns. They usually contain salicylic acid 12.6-40% as a pad or solution. Urea 20-50%, silver nitrate, and hydrocolloid dressings can also be used for this condition.
More recently, hydrocolloid dressings that have a hydrating effect on the skin have been evaluated as the potential treatment of keratotic lesions. However, keratolytic agents must be used with caution, as overapplication can cause chemical burns.
Remember: Neuropathic and immunocompromised patients should avoid these agents.
-
Gentle paring (cutting off), debridement, or enucleation: Pain associated with a callosity can be relieved to a certain extent by sharp debridement to reduce the amount of hyperkeratotic tissue.
This procedure involves cutting off the lesion with a sharp scalpel blade and removing the central keratin plug (on underlying nerves in the papillary layer), with the use of local anesthetic if necessary.
It reduces the pressure on underlying dermal nerves, thus alleviating the pain. Also, recurrence can be prevented by gently trimming the lesion (after soaking the lesion in warm water for 20 minutes) using a pumice stone.
-
Laser therapy: The 2,940 nm erbium-doped yttrium aluminum garnet laser has been used to treat corns with minimal thermal tissue damage. The carbon dioxide laser has also been reported to be efficient. However, if the trigger factors are maintained, it might lead to recurrence of lesions in some patients.
-
Cushioning and foot biomechanics/Orthoses: Cushioning and altering foot biomechanics can help prevent corns and treat the existing ones.
Orthotic devices are often prescribed to redistribute mechanical forces in the foot and allow a lesion to heal. There are various types of orthoses, including doughnut-shaped corn pads, heloma shields, and silicone toe splints, that relieve pressure from the tender central core in corns.
In addition, silicone sleeves release mineral oil, thereby softening the lesion. Interdigital wedges made of plastazote (a foam padding) or orthodigital splints made of silicone promote healing of an interdigital soft corn.
-
Surgery: Various surgical options are available for those patients in whom conservative measures have not worked. In rare cases, surgery to correct an underlying problem of bone structure may be needed to treat a corn or callus that keeps returning and is not relieved by padding, shoe inserts, and periodic shaving.
Note: Diabetic patients with corns and calluses need to be wory, as attempting any treatment of corns on their own may lead to excessive trimming and ultimately abrasion of the skin. Treatment should strictly be done by a specialist only.
Home-care For Corns
Before treating corn, first evaluate the cause of friction. In many cases, they’ll go away on their own when the pressure or friction causing them stops. If protecting the corns from further irritation doesn’t solve your problem, podiatrist or GP may recommend the following home-care tips to get rid of them:
Soak the affected area in warm water
You can soak the corn or callus in warm water for about 15-20 minutes or till the skin gets soft.
File or pumice the surface
You can file the corn and callus using a pumice stone. First you need to soak the pumice stone in warm water for sometime and then use it in circular or sideways motions gently to file the corn or callus.
Do not take off much skin
You should be careful and not file the skin excessively, as it might lead to bleeding and infection also.
Keep the toenails trimmed
Long toenails can push against your shoe, causing a corn to form over time. Keep your toenails trimmed to remove this pressure.
Use padding
You can surround the corn with donut-shaped adhesive pads to prevent it from making contact with the shoes. Likewise for calluses, you can cushion the affected area with moleskin to relieve pressure or further irritation.
You can also make a "donut" with moleskin, lamb's wool, felt, or foam. Many pharmacies sell over-the-counter products to cushion corns and calluses.
Wear properly fitted shoes
Tight shoes are the main cause of corns and calluses. It is advised to wear low-heeled shoes and choose shoes that aren’t too loose or tight. This reduces the irritation that caused the problem in the first place.
Moisturize the skin regularly
Use moisturizing lotion or cream with salicylic acid, ammonium lactate, or urea. These ingredients gradually soften the hard corns and calluses.
If you want to know more about home-care for corns and calluses.
Complications Of Corns
Though corns appear to be a minor health problem, they can take a severe shape if not treated in due time.
Complications might include:
-
Pain
-
Tinea pedis (a fungal skin infection that usually begins between the toes)
-
Ulceration and infection
-
Septic arthritis
-
Osteomyelitis
Post-surgical complications include:
-
Digital swelling
-
Numbness
-
Infection
-
Floppy or flail toe
-
Deformity recurrence
-
Joint and toe stiffness
Living With Corns
Usually corns and calluses aren’t a serious problem, but these minor nuisances can interfere with everyday work. Therefore, it is important to manage them timely.
Consider the following general strategies and tips to manage corns and calluses:
-
Calluses on hands can usually be prevented by wearing gloves while indulging in certain activities, such as when gardening or lifting weights.
-
Calluses on feet can usually be prevented by wearing shoes and socks that fit well.
-
Corns on feet can be prevented by wearing shoes that have a wider toe box.
-
Wear gloves while using tools, such as a garden spade or rake.
-
Wear appropriate padding if you expose other parts of your body to friction. For example, if you are on your knees laying carpet, wear knee pads.
A podiatrist may be able to help you make changes that can manage and prevent their occurrence.
In addition, foot problems are common in people with diabetes. You can prevent diabetes-related foot problems by taking care of your feet every day. Managing your blood glucose levels, also called blood sugar, can also help keep your feet healthy.
Over time, diabetes may cause nerve damage, also called diabetic neuropathy, that can cause tingling and pain, and can also numb feeling in your feet. When you lose feeling in your feet, you may not feel a pebble inside your sock or a blister on your foot, which can lead to cuts and sores. These cuts and sores can also become infected. Hence, special care is paramount for diabetic patients.
Here are a few things that you can do every day to keep your feet healthy:
-
Check your feet every day.
-
Wash your feet every day.
-
Smooth corns and calluses gently.
-
Trim your toenails straight across.
-
Wear shoes and socks at all times.
-
Protect your feet from hot and cold.
-
Get a foot check at every health care visit.