- TOP CITIES
- New Delhi
- Gurgaon
- Pune
- Mumbai
- Bengaluru
- Kolkata
- Hyderabad
- Ahmedabad
- Chennai
- Indore
- Lucknow
- Jaipur
- Chandigarh
- Bhopal
- Noida
- Navi Mumbai
- Surat
- Patna
- Ludhiana
- Bhubaneshwar
- ALL CITIES
- Abohar
- Adilabad
- Adoni
- Agar
- Agartala
- Agra
- Ahmedabad
- Ahmednagar
- Aizawl
- Ajmer
- Akola
- Alappuzha
- Aligarh
- Alipurduar
- Alirajpur
- Allahabad
- Almora
- Alwar
- Ambala
- Ambattur
- Ambedkar Nagar
- Amravati
- Amreli
- Amritsar
- Amroha
- Anand
- Anantapur
- Ananthnag
- Anantnag
- Angamally
- Angul
- Ankleshwar
- Annur
- Anuppur
- Arakkonam
- Arambag
- Arantangi
- Araria
- Arcot
- Ariyalur
- Arwal
- Asansol
- Ashok Nagar
- Assaudh
- Attuvampatti
- Auraiya
- Aurangabad Bihar
- Aurangabad Maharashtra
- Aviyur
- Ayyangarkulam
- Azamgarh
- Badlapur
- Bagalkot
- Bageshwar
- Baghpat
- Bagpat
- Bahadurgarh
- Bahraich
- Baksa
- Balaghat
- Balangir
- Baleswar
- Ballia
- Bally
- Balrampur
- Banaskantha
- Banda
- Bangalore
- Bangalore Rural
- Banka
- Bankura
- Banswara
- Barabanki
- Baramati
- Baramulla
- Baran
- Baraut
- Bardhaman
- Bareilly
- Bargarh
- Barmer
- Barnala
- Barpeta
- Barrackpore
- Baruipur
- Barwani
- Basirhat
- Bastar
- Basti
- Bathinda
- Beawar
- Beed
- Begumganj
- Begusarai
- Behraghora
- Behrampur
- Belgaum
- Bellary
- Belur
- Bengaluru
- Betul
- Betul Ganj
- Bhadrak
- Bhadravati Karnataka
- Bhagalpur
- Bhandara
- Bharatpur
- Bharuch
- Bhatkal
- Bhavani
- Bhavnagar
- Bhilai
- Bhilwara
- Bhind
- Bhiwadi
- Bhiwandi
- Bhiwani
- Bhojpur
- Bhopal
- Bhubaneshwar
- Bhuna
- Bhusawal
- Bidar
- Bijapur Chattisgarh
- Bijapur Karnataka
- Bijnor
- Bikaner
- Bilaspur Chattisgarh
- Bilaspur Himachal Pradesh
- Birbhum
- Bishnupur
- Boisar
- Bokaro
- Bongaigaon
- Bongaon
- Botad
- Boudh
- Budaun
- Budgam
- Bukkapatnam
- Bulandshahr
- Buldana
- Buldhana
- Bundi
- Burdwan
- Burhanpur
- Buxar
- Cachar
- Calicut
- Chamarajanagar
- Chamba
- Chamoli
- Champawat
- Champhai
- Chandauli
- Chandel
- Chandigarh
- Chandrapur
- Changanassery
- Changlang
- Chatra
- Chennai
- Chhatarpur
- Chhindwara
- Chikkaballapur
- Chikkaballapura
- Chikmagalur
- Chintamani
- Chitradurga
- Chitrakoot
- Chittoor
- Chittorgarh
- Chrompet
- Churachandpur
- Churu
- Cochin
- Coimbatore
- Cooch Behar
- Cuddalore
- Cuddapah
- Cuttack
- Dadra & Nagar Haveli
- Dahanu
- Dahod
- Dakshina Kannada
- Daman
- Damoh
- Dantewada
- Darbhanga
- Darjiling
- Darrang
- Datia
- Dausa
- Davangere
- Debagarh
- Dehradun
- Delhi
- Deoghar
- Deoria
- Dera Bassi
- Devanahalli
- Dewas
- Dhakaoli
- Dhalai
- Dhamtari
- Dhanbad
- Dhar
- Dharmapuri
- Dharwad
- Dhemaji
- Dhenkanal
- Dholpur
- Dhone
- Dhubri
- Dhule
- Dhully
- Dibang Valley
- Dibrugarh
- Dibrugarh Tamil Nadu
- Dimapur
- Dindigul
- Dindori
- Dispur
- Diu
- Doda
- Dombivli
- Dombivli Station
- Dumka
- Dungarpur
- Durg
- Durgapur
- East Champaran
- East Garo Hills
- East Godavari
- East Kameng
- East Khasi Hills
- East Midnapore
- East Nimar
- East Siang
- East Sikkim
- East Singhbhum
- Ellanaickenpatti
- Ernakulam
- Erode
- Etah
- Etawah
- Faizabad
- Faridabad
- Faridkot
- Farrukhabad
- Fatehabad
- Fatehgarh Sahib
- Fatehpur
- Fazilka
- Firozabad
- Firozpur
- Gadag
- Gadarwara
- Gadchiroli
- Gajapati
- Gandhinagar
- Ganganagar
- Gangtok
- Ganjam
- Garhwa
- Gariaband
- Gautam Buddha Nagar
- Gaya
- Ghaziabad
- Ghazipur
- Gir Somnath
- Giridh
- Goa
- Goalpara
- Gobichettipalayam
- Godda
- Golaghat
- Golaniya
- Gonda
- Gondia
- Gopalganj
- Gorakhpur
- Greater Noida
- Greater Thane
- Gulbarga
- Gumla
- Guna
- Guntur
- Gurdaspur
- Gurgaon
- Guwahati
- Gwalior
- Hailakandi
- Halol
- Hamirpur Himachal Pradesh
- Hamirpur Uttar Pradesh
- Hansi
- Hanumangarh
- Hapur
- Harapanahalli
- Harda
- Hardoi
- Haridwar
- Hassan
- Hathras
- Haveri
- Hazaribag
- Hazaribagh
- Hinauti
- Hindaun
- Hingoli
- Hisar
- Hojai
- Hooghly
- Hosakote
- Hoshangabad
- Hoshiarpur
- Hoskote
- Hospet
- Hosur
- Howrah
- Hubli
- Hyderabad
- Ichalkaranji
- Idukki
- Imphal
- Imphal East
- Imphal West
- Indore
- Itanagar
- Jabalpur
- Jagatsinghapur
- Jaintia Hills
- Jaipur
- Jaisalmer
- Jajapur
- Jalandhar
- Jalaun
- Jalgaon
- Jallipatti
- Jalna
- Jalore
- Jalpaiguri
- Jammu
- Jamnagar
- Jamshedpur
- Jamtara
- Jamui
- Janjgir-Champa
- Jashpur
- Jaunpur
- Jayamala
- Jehanabad
- Jhabua
- Jhajjar
- Jhalawar
- Jhansi
- Jhargram
- Jharsuguda
- Jhujhunu
- Jind
- Jodhpur
- Jorhat
- Junagadh
- Jyotiba Phule Nagar
- Kachchh
- Kadamakkudy
- Kadapa
- Kadiri
- Kadthal
- Kaghaz Nagar
- Kaimur Bhabua
- Kaithal
- Kakinada
- Kalahandi
- Kalipahari
- Kallakurichi
- Kalligudi
- Kalyani
- Kamrup
- Kanadukathan
- Kanchipuram
- Kandhamal
- Kandukur
- Kangra
- Kanker
- Kannauj
- Kannur
- Kanpur
- Kanpur Dehat
- Kanpur Nagar
- Kansapuram
- Kanyakumari
- Kapurthala
- Karad
- Karaikal
- Karaikudi
- Karatholuvu
- Karauli
- Karbi Anglong
- Kargil
- Karimganj
- Karimnagar
- Karnal
- Karupatti
- Karur
- Karwar
- Kasaragod
- Kathua
- Katihar
- Katni
- Kattupakkam
- Kaushambi
- Kavaratti
- Kawardha
- Kendrapara
- Kendujhar
- Khagaria
- Khammam
- Khandwa
- Khanna
- Kharagpur
- Khargone
- Kheda
- Kheri
- Khorda
- Kichha
- Kinnaur
- Kiphire
- Kishanganj
- Kochi
- Kodagu
- Kodaikanal Observatory
- Koderma
- Kohima
- Kokrajhar
- Kolar
- Kolasib
- Kolhapur
- Kolkata
- Kollam
- Kooram
- Koppal
- Koraput
- Korba
- Koriya
- Kota
- Kothakudi
- Kothur
- Kottayam
- Kovilpatti
- Koyilandy
- Kozhikode
- Krishna
- Krishnagiri
- Kulgam
- Kullu
- Kumbakonam
- Kumburvayal
- Kundli
- Kupwara
- Kurnool
- Kurukkalpatti
- Kurukshetra
- Kurung Kumey
- Kushinagar
- Kutch
- Laddivadi
- Lahul & Spiti
- Lakhimpur
- Lakhisarai
- Lakshadweep
- Lalitpur
- Lambakheda
- Latehar
- Latur
- Lawngtlai
- Leh
- Lohardaga
- Lohit
- Lonavala
- Longleng
- Lower Dibang Valley
- Lower Subansiri
- Lucknow
- Ludhiana
- Lunglei
- Machur
- Madhepura
- Madhubani
- Madhupur
- Madikeri
- Madurai
- Mahabubabad
- Mahabubnagar
- Mahadanapuram
- Maharajganj
- Mahasamund
- Mahbub Nagar
- Mahe
- Mahendragarh
- Mahoba
- Mainaguri
- Mainpuri
- Majuli
- Malappuram
- Malda
- Malkangiri
- Malout
- Mammit
- Manakudi
- Manapparai
- Manawar
- Mandi
- Mandi Gobindgarh
- Mandla
- Mandsaur
- Mandya
- Mangalore
- Manipal
- Mannargudi
- Mansa
- Margao
- Marigaon
- Mathura
- Mau
- Mayurbhanj
- Medak
- Meenkashipuram
- Meerut
- Mehsana
- Melaparuthigudi
- Melpallam
- Melpattamkarisalkulam
- Melvisharam
- Midnapore
- Mirzapur
- Moga
- Mohali
- Mohanur
- Mokokchung
- Mon
- Moradabad
- Morena
- Muchipara
- Mughal Sarai
- Muktsar
- Mumbai
- Mumbai Extension
- Munger
- Murshidabad
- Muzaffarnagar
- Muzaffarpur
- Mysore
- Nabarangapur
- Nadia
- Nadiad
- Naduvakurichi
- Nagaon
- Nagapattinam
- Nagaur
- Nagpur
- Naidupuram
- Nainital
- Najibabad
- Nalanda
- Nalbari
- Nalgonda
- Namakkal
- Nanded
- Nandurbar
- Narayanpur
- Narmada
- Narnaul
- Narsinghpur
- Narsipatnam
- Nashik
- Navi Mumbai
- Navsari
- Nawada
- Nawanshahr
- Naxalbari
- Nayagarh
- Neemrana
- Neemuch
- Nelamangala
- Nellore
- Nerur
- New Delhi
- Nicobar
- Nilgiri
- Nilgiris
- Nizamabad
- Noida
- North 24 Parganas
- North And Middle Andaman
- North Cachar Hills
- North Dinajpur
- North Goa
- North Sikkim
- North Tripura
- Nowda
- Nuapada
- Nuh
- Nuvem
- Ooty
- Osmanabad
- Pakur
- Palakkad
- Palamalai
- Palamu
- Palani
- Palghar
- Pali
- Pambakovil Shandy
- Panaji
- Panchkula
- Panchmahal
- Panipat
- Panna
- Panvel - Station
- Papanasam
- Pappankulam
- Pappinaickenpatti
- Papum Pare
- Paradip
- Parbhani
- Pasumpon
- Patan
- Pathanamthitta
- Pathankot
- Patiala
- Patna
- Pauri Garhwal
- Pavitram
- Perambalur
- Peren
- Phalghat
- Phek
- Pilani
- Pilibhit
- Pinnathur
- Pithoragarh
- Pondicherry
- Ponga
- Poonamalle
- Poonch
- Porbandar
- Port Blair
- Prakasam
- Pratapgarh
- Proddatur
- Pudukkottai
- Pulankurichi
- Pulavadi
- Puludipatti
- Pulwama
- Pune
- Pungamuthur
- Purba Bardhaman
- Purbasthali
- Puri
- Purnia
- Puruliya
- Puzhal
- Quilon
- Raebareli
- Raichur
- Raigad Maharashtra
- Raigarh Chattisgarh
- Raikasba
- Raipur
- Raisen
- Rajahmundry
- Rajauri
- Rajgangpur
- Rajgarh
- Rajkot
- Rajnandgaon
- Rajpura
- Rajsamand
- Ramanagar
- Ramanathapuram
- Ramgarh
- Rampur
- Ranchi
- Rangareddi
- Rangareddy
- Ranipet
- Ratlam
- Ratnagiri
- Raurkela
- Rayagada
- Reasi
- Rewa
- Rewari
- Ri Bhoi
- Rishikesh
- Rohtak
- Rohtas
- Roorkee
- Ropar
- Rourkela
- Rudraprayag
- Rudrapur
- Rupnagar
- Rurka Kalan
- S.A.S. Nagar
- Sabarkantha
- Sagar
- Saharanpur
- Saharsa
- Sahibganj
- Saiha
- Salem
- Samastipur
- Sambalpur
- Sambhal
- Sangareddy
- Sangli
- Sangrur
- Sant Kabir Nagar
- Sant Ravidas Nagar
- Saran
- Satara
- Satna
- Sawai Madhopur
- Secunderabad
- Sehore
- Senapati
- Seoni
- Seraikela-Kharsawan
- Serchhip
- Shahapur
- Shaharanpur
- Shahdol
- Shahjahanpur
- Shahpura
- Shajapur
- Shamshabad
- Sheikhpura
- Sheohar
- Sheopur
- Shikohabad
- Shillong
- Shimla
- Shimoga
- Shivpuri
- Shrawasti
- Shyamnagar
- Sibmandir
- Sibsagar
- Siddharthnagar
- Sidhi
- Sihora
- Sikar
- Siliguri
- Silvassa
- Simdega
- Simga
- Sindhudurg
- Singrauli
- Sirkaali
- Sirmaur
- Sirohi
- Sirsa
- Sitamarhi
- Sitapur
- Sivaganga
- Sivakasi
- Sivasagar
- Siwan
- Solan
- Solapur
- Sonapur
- Sonarpur
- Sonbhadra
- Sonipat
- Sonitpur
- Soro
- South 24 Parganas
- South Andaman
- South Dinajpur
- South Garo Hills
- South Goa
- South Sikkim
- South Tripura
- Sricity
- Srikakulam
- Srinagar
- Subarnapur
- Sujangarh
- Sultanpur
- Sundergarh
- Supaul
- Surat
- Surendranagar
- Surguja
- T Pudupatti
- Tadipatri
- Talasari
- Tamenglong
- Tapi
- Tarn Taran
- Tawang
- Tehri Garhwal
- Tenkasi
- Thane
- Thanjavur
- The Dangs
- Theni
- Thimmarajanpettai
- Thirukkalukundram
- Thirukkannamangaikottam
- Thiruvaiyaru
- Thiruvarur
- Thoothukudi
- Thoubal
- Thrissur
- Thungavi
- Tikamgarh
- Timarni
- Tinsukia
- Tirap
- Tiruchendur
- Tiruchirappalli
- Tiruklalikundram
- Tirumani
- Tirunelveli
- Tirupati
- Tiruppur
- Tirupur
- Tirur
- Tiruttani
- Tiruvalla
- Tiruvallur
- Tiruvannamalai
- Tiruvarur
- Titilagarh
- Tohana
- Tonk
- Trimulgherry
- Trivandrum
- Tuensang
- Tumkur
- Turaiyur Koitpatti
- Tuticorin
- Udaipur Rajasthan
- Udaipur Tripura
- Udayarpalayam
- Udham Singh Nagar
- Udhampur
- Udupi
- Ujjain
- Ukhrul
- Umaria
- Una
- Unnao
- Upper Siang
- Upper Subansiri
- Uttara Kannada
- Uttarkashi
- Vadagarai
- Vadakara
- Vadodara
- Vaishali
- Valsad
- Vandavasi
- Vapi
- Varanasi
- Vattur
- Vellore
- Vidisha
- Vijayawada
- Vikarabad
- Villupuram
- Virudhunagar
- Visakhapatnam
- Visalakshi Nagar
- Vizianagaram
- Warangal
- Wardha
- Washim
- Wayanad
- West Champaran
- West Garo Hills
- West Godavari
- West Kameng
- West Khasi Hills
- West Midnapore
- West Nimar
- West Siang
- West Sikkim
- West Singhbhum
- West Tripura
- Wokha
- Y.S.R.
- Yadgir
- Yamunanagar
- Yavatmal
- Zunhebotto
Want to know more?
Read Our Editorial PolicyHave issue with the content?
Report Problem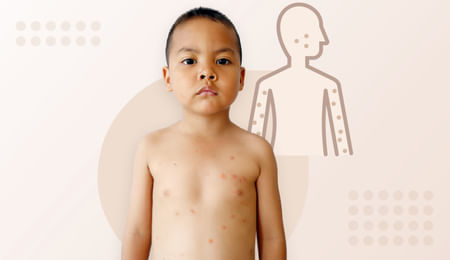
Mpox (Monkeypox)
Overview
Mpox, previously known as Monkeypox is a viral zoonotic disease, which means that the monkeypox virus causes the disease, and the infection spreads from animals to humans.
Infection is transmitted to humans through scratches or bites from infected rodents such as rats, mice, and squirrels or by eating bush meat. Transmission of the virus can also happen from human to human but is limited to close household contacts or health care workers not wearing personal protective equipment.
Mpox was discovered in 1958 when two outbreaks of a pox-like disease occurred in groups of monkeys being used for research. The disease was first discovered in monkeys, hence the name monkeypox.
Mpox is commonly found in central and west Africa. Still, cases have been identified in other countries outside of central and west Africa, following travel from regions where Mpox is endemic.
This disease typically presents with fever and rash and is usually a mild and self-limiting disease. Most patients with mild cases recover without medical intervention. This information can help alleviate unnecessary fear and panic among the public.
Key Facts
- All age groups
- Both men and women
- Skin
- Mouth
- Muscles
- Lymph nodes
- Smallpox
- Chickenpox
- Rickettsialpox
- Scabies
- Secondary syphilis
- Yaws
- Measles
- Generalized vaccinia
- Disseminated zoster
- Bacterial skin infections
- Drug-associated eruption
- Eczema herpeticum
- Disseminated herpes simplex
- Chancroid
- Hand foot mouth disease
- Infectious mononucleosis
- Molluscum contagiosum
- Molecular analysis: Virus isolation & Electron microscopy
- Blood analysis: Real-time polymerase chain reaction (PCR), Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) & Immunofluorescent antibody assay
- Urine analysis
- Supportive care: Antipyretics, antiemetics & antihistamines
- Medical management: Antivirals, Tecovirimat, Brincidofovir & Cidofovir
- General physician
- Infectious disease specialist
- Internal medicine specialist
Symptoms Of Mpox
Mpox symptoms in humans, while similar to smallpox, are milder. The key symptom that sets it apart from smallpox is the enlargement or swelling of the lymph nodes. This distinction should provide some reassurance about the severity of the illness.
The time from infection to symptoms for Mpox is usually 6-13 days but can range from 5−21 days.
Predom symptoms (0-5 days):
- Fever
- Headache
- Myalgia (muscle aches)
- Backache
- Lymphadenopathy
- Chills
- Malaise (tiredness)
- Exhaustion
- Sore throat
- Dry cough
- Dyspnea (shortness of breath)
Progression of the disease
- Lesions appear within 1 to 3 days after the appearance of fever on the tongue and mouth.
- The patient generally develops a rash, often beginning on the face and spreading to other body parts within 24 hours.
- By the 4th to 5th day, the lesions become raised and filled with pus.
- By the end of the 2nd week, they dry up and crust. The scabs usually remain for a week before they start to fall off.
This illness typically lasts for about 2-4 weeks, and lesions progress through the following stages:
- Macular stage: Flat, discolored spots appear on the skin.
- Papular stage: The spots become raised and firm.
- Vesicular stage: Lesions develop into small, fluid-filled blisters.
- Pustular stage: The blisters fill with pus and become more pronounced.
- Scabbing stage: Lesions dry out, form scabs, and eventually fall off.
Remember, the severity of the skin manifestation of Mpox depends on vaccination status, age, nutrition status, and immunity status. If all the news about Mpox has you worried, remember that the symptoms are generally mild. There is no need to panic. Continue reading to get all your queries answered about Mpox.
Causes Of Mpox
Mpox is caused by the monkeypox virus that belongs to the Poxviridae family. It is generally acquired through rodents such as rats, mice, and squirrels (who are the carrier of the virus) in parts of West and Central Africa.
Any person can get Mpox by the following ways:
-
Bite from an infected animal or touching its blood, body fluids, spots, blisters, or scabs.
-
Eating meat of an infected animal from Central or West Africa that has not been cooked thoroughly.
-
Touching the skin or fur of the infected animals.
Transmission
The Mpox virus mainly causes animal-to-human transmission. In rare cases, human-to-human transmission is also possible when there is close contact or large respiratory droplets.
Animal-to-human transmission
- Direct physical contact with the infected blood, body fluids, skin lesions, blisters, or scabs from an infected animal.
- Eating the meat of an infected animal that is not cooked thoroughly.
- A bite or scratch from animals like rats or squirrels infected by the virus.
Human-to-human transmission
- Close physical contact with a person infected by Mpox virus
- Contamination with the virus such as clothes, bedding, or towels by touching
- Saliva or respiratory droplets while by coughing or sneezing
- The placenta from mother to fetus
- Mother to baby during and after childbirth
- Unprotected sex with an infected person
- Man-to-man sex
Condoms are known to protect against a wide range of sexually transmitted diseases (STDs). Understand nine common mistakes while using a condom and how to prevent them.
Risk Factors For Mpox
Anyone who has close physical contact with an infected animal or someone who has symptoms of Mpox is at the highest risk of developing the infection. Other people, who are at a greater risk of developing serious symptoms from Mpox include:
-
Newborns
-
Children
-
Immuno-deficient patients
-
Patients with a history of chronic illness
-
Healthcare workers
-
Laboratory professionals
Diagnosis Of Mpox
The investigation should consist of the following:
-
Examining the patients clinically using appropriate infection prevention and control (IPC) measures.
-
Questioning the patient about possible sources of infection and the presence of similar disease or symptoms in the patient’s community and contacts.
-
Collecting and dispatching the specimens safely for laboratory examination of Mpox.
If Mpox is suspected, health workers collect an appropriate sample and transport it safely to a laboratory with proper capability.
-
Samples are usually collected from a person showing symptoms, especially a traveler from a region where Mpox is endemic, an outbreak or a community(person-to-person) spread.
-
Asymptomatic travelers are observed for 21 days, and samples are collected once signs and symptoms appear.
The various clinical samples that can be collected to make the diagnosis are:
1. During rash phase
-
Nasopharyngeal and oropharyngeal swabs or lesions from the roof, base scraping, fluid, and crust or scab.
-
Blood in specialized tubes like EDTA and SSGT
-
Urine in sterile container
2. During the recovery phase
Additional tests are conducted to ensure the patient has fully recovered and is no longer infectious. These tests include blood in an EDTA/SSGT tube and urine in a sterile container.
-
Blood in an EDTA/ SSGT tube
-
Urine in a sterile container
For the confirmation of Mpox on the suspected clinical specimens(Blood/ Lesion/ swabs/ urine):
a) PCR for Orthopoxvirus genus [Cowpox, Buffalopox, Camelpox, Mypox] is done.
b) If the specimen shows positivity for the Orthopoxvirus, it would be further confirmed by Mpox-specific conventional PCR or real-time PCR for Mpox DNA.
c) Additionally, virus isolation and the Next Generation Sequencing of clinical samples might be used for the characterization of the positive clinical specimens.
Get your lab tests done with us, where patient comfort and safety are the utmost priority.
Prevention Of Mpox
Mpox prevention depends on decreasing human contact with infected animals and limiting person-to-person spread. Mpox can be prevented by following these measures:
-
Avoid contact with infected animals, especially sick or dead ones.
-
Cook all foods that contain animal meat or parts thoroughly.
-
Avoid any kind of contact with bedding and other materials contaminated with the virus.
-
Maintain hygiene by washing your hands with soap and water or alcohol hand rub after coming into contact with an infected animal or person or handling their products.
-
Avoid close contact with an infected person.
-
Use personal protective equipment (PPE) when caring for an infected person.
-
Get vaccinated.
Humans have a close connection with microorganisms. Viruses are tiny microorganisms that range in size from about 20 to 400 nanometers in diameter. Read how viruses are transmitted and ways to prevent them.
Vaccination for Mpox?
JYNNEOS TM, also known as Immune or Imvanex, is a live attenuated (weakened) virus vaccine that has been approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for the prevention of mpox. However, it is not yet widely available.
Smallpox vaccines can protect against Mpox. Certain countries require timely vaccination of close contacts as post-exposure prophylaxis or for certain groups of health care workers as pre-exposure vaccination.
However, after 1980, when WHO declared that smallpox was eradicated globally, no vaccine has been manufactured in India.
Thinking about why adults would need vaccinations? Read this to know the most common vaccinations that adults require.
Specialist To Visit
If any person develops a rash, accompanied by fever, discomfort or illness, along with swollen lymph nodes, they should contact their doctor and get tested for Mpox. Doctors who can help treat the symptoms and diagnose Mpox are:
- General physician
- Infectious disease specialist
- Internal medicine specialist
The general physician plays a crucial role in managing Mpox by diagnosing, providing symptomatic treatment, advising on isolation, and most importantly, referring severe cases for specialized care.
The infectious disease specialist, with their specialized knowledge and skills, is instrumental in managing Mpox. They offer expert diagnosis, advanced treatment options, and guidance on preventing the spread of the virus.
The internal medicine specialist provides comprehensive care in managing Mpox. They address symptoms and coordinate treatment plans for the infection, ensuring a holistic approach to patient care.
If you are facing any health issues, seek advice from our team of doctors.
Treatment Of Mpox
Before undertaking the treatment of Mpox lets learn about the protocol for handling suspected Mpox patients first:
Protocol for handling patients with suspected Mpox
Suspected patients should be referred there for further evaluation and treatment.
Patient Handling and Isolation:
-
Patients must be handled with strict infection control measures.
-
Staff should use personal protective equipment (PPE) when dealing with suspected cases.
-
Upon arrival, patients with fever, rash, or contact with confirmed Mpox cases should be assessed immediately.
-
Key symptoms to identify include fever, headache, muscle aches, back pain, swollen lymph nodes, chills, exhaustion, and specific skin lesions like rash that can develop into vesicles and pustules.
Isolation/Holding Area:
-
Suspected patients should be placed in a designated isolation area to avoid contact with others.
-
Beds are reserved for isolating Mpox patients, based on the emergency recommendation.
-
These beds serve as temporary holding areas until the patient is transferred to definitive care.
Notification to IDSP:
-
Notify the Integrated Disease Surveillance Programme (IDSP) at 8745011784
-
Provide patient details, history, clinical findings, and contact information to the IDSP.
Treatment of Mpox
Currently, there are no specific clinically proven treatments for Mpox infection. However, it's important to note that Mpox is usually a mild and self-limiting disease. Most patients with mild diseases recover without medical intervention, instilling a sense of hope and optimism. The treatment and management mainly involve the following:
Supportive care
Skin rash
-
Not touching or scratching the lesions can worsen the rash and increase the risk of infections.
-
Cleaning the area with an antiseptic ointment such as mupirocin acid or fucidin and covering the lesion with light dressing
-
In case of a secondary bacterial infection, antibiotics may be prescribed. It's important to use antibiotics as directed by a healthcare professional to prevent antibiotic resistance.
Ulcers
-
Sitz bath for genital ulcers
-
Warm salt gargling and use of topical oral anti-inflammatory gel for mouth ulcers.
Dehydration
-
Taking adequate fluids like juices and ORS
-
Eating a balanced, nutrient-rich diet
-
In severe cases, intravenous drip may be required
Here's more on what to do if you feel dehydrated.
Other symptoms
-
Paracetamol for fever.
-
Antiemetics like Ondansetron and Metachlopramide for nausea and vomiting.
-
Antihistamines like Cetirizine for itching.
Medical management
Certain cases of Mpox are treated with the following:
-
Antivirals: Several antivirals may be helpful in the treatment of Mypox. These drugs were approved for treating smallpox based on animal models but are expected to have the same effect on human Mpox.
-
Tecovirimat: It is a potent inhibitor of an orthopoxvirus protein. The recommended dose of t depends upon the patient's weight.
-
Brincidofovir: This drug was approved in June 2021 for use in the United States to treat smallpox and can also be used for Mpox.
-
Cidofovir: The drug shows promise by effectively combating Mpox in lab tests and protecting animals from severe infection.
Home-care For Mpox
Home management guidelines for non-hospitalized patients
-
Isolation: Keep the patient in a separate room; limit contact with other family members.
-
No Leaving Home: The patient should stay home unless seeking medical care.
-
No Visitors: Do not allow visitors in the home.
-
Masking: Patients with respiratory symptoms should wear a surgical mask; others may wear masks when near the patient.
Get much-needed protection from infections and pollution with our well-curated range of masks.
-
Gloves: Use disposable gloves for direct contact with lesions and dispose of them properly.
Looking for some good-quality gloves?
-
Cover Lesions: Cover skin lesions (e.g., long sleeves, pants) to reduce contact risk.
-
Waste Disposal: Contain and dispose of contaminated waste in biomedical waste bags.
-
Hand Hygiene: Wash hands with soap and water or use alcohol-based hand rub after touching lesions or contaminated items.
-
Laundry Care: Wash soiled laundry in warm water; handle carefully to avoid spreading infection.
-
Utensils: Do not share dishes or eating utensils; wash them thoroughly after use.
-
Surface Disinfection: Clean and disinfect contaminated surfaces using standard household products.
-
Pets: Keep pets and domestic animals away from the patient's environment.
Masks have proven to be a powerful tool in our fight against infectious diseases, providing a crucial layer of protection. With cases of Mpox increasing around the world, the correct use of masks is more important than ever, offering reassurance and confidence in our ability to prevent the spread of disease.
Complications Of Mpox
People with Mpox are infectious to others from the onset of fever until all lesions scab over. Mpox complications include:
-
Dehydration due to:
-
Sepsis (reaction to an infection that causes widespread inflammation in the body)
-
Bacterial superinfection of skin
-
Permanent skin scarring
-
Hyperpigmentation or hypopigmentation of skin
-
Permanent scarring of the cornea (vision loss)
-
Encephalitis (inflammation of the brain)
-
Shortness of breath, chest pain, difficulty in breathing
-
Altered consciousness
-
Seizures
-
Decrease in urine output
-
Lethargy
Living With Mpox
With the increase in cases, the stigma around Mpox is bound to increase. Social stigma is generally a negative association between a person or group of people with certain characteristics of a specific disease. It may mean that people are labelled, stereotyped, discriminated against, treated separately, and experience loss of status because of a perceived link with a disease, especially during an outbreak. This can negatively affect the patients and their caregivers, family, and friends.
The current increase in Mpox cases and media coverage can also lead to stress and anxiety in patients and their family members. Here are some tips to deal with the psychological effects of the same:
-
Do not believe the experiences of others all the time
-
Talk about the mental health issues with healthcare professionals
-
Do not hide away or isolate yourself from the world
-
Reach out to family, friends, and life coaches for support
-
Get help from a therapist or psychologist if needed
-
Join a mental health support group if required
-
Understand it’s not personal
Mpox is causing similar uncertainty amongst the people as COVID-19 had caused during its inception.
Read more about COVID-19.
Frequently Asked Questions
References
- Moore M, Zahra F. Monkeypox. [Updated 2022 May 22]. In: StatPearls [Internet]. Treasure Island (FL): StatPearls Publishing; 2022 Jan.
- What is Monkeypox? Monkeypox. World Health Organization. May 2022.
- Signs and Symptoms. Monkeypox. Center For Disease Control and Prevention. July 2021.
- How Do You Get Monkeypox? Monkeypox. NHS UK. June 2022.
- Guidelines for the management of monkeypox.Ministry of Health and Family Welfare. GOVERNMENT OF INDIA
- Khodasevich L, Jezek Z, Messinger D. Monkeypox virus: ecology and public health significance. Bull World Health Organ. 1988.
- Outbreak at a glance. Multi-country monkeypox outbreak in non-endemic countries: Update. World Health Organization.May 2022.
- Mauldin EA, Peters-Kennedy J. Integumentary System. Jubb, Kennedy & Palmer's Pathology of Domestic Animals: Volume 1. 2016:509–736.e1.
- Mpox [Internet]. Who.int. [cited 2024 Aug 27].