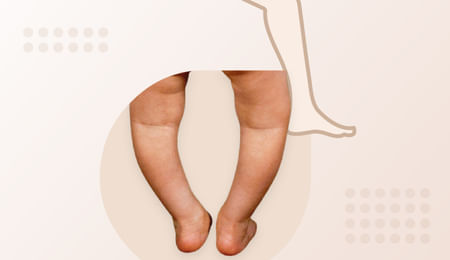
Rickets
Rickets is a medical condition commonly seen in children. It is characterized by bowed legs and a curved spine, which causes a lot of pain and discomfort. Depending on the type of rickets your child develops, it can be hereditary (genetic in nature) or acquired (because of low consumption of essential nutrients).
Mainly, a lack of essential nutrients such as Vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus have been attributed to the development of rickets. Other factors such as living in cold countries, having dark skin, and genetics can also increase the risk of developing rickets.
Mostly seen in children between the ages of 6 months to 2 years, your child can combat the symptoms of rickets with Vitamin D and calcium supplements and high exposure to sunlight.
Rickets can be prevented by proper exposure to sunlight and having a diet rich in Vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus. It can also be treated by taking Vitamin D supplements and exposure to sunlight.
- Children between 6 months to 2 years of age
- Both men and women
- Spine
- Bones
- Legs
- Skeleton
- Osteomalacia
- Osteogenesis imperfecta
- Primary hypoparathyroidism
- Lowe syndrome
- Fanconi syndrome
- Scurvy
- Bone X-rays
- Blood tests
- Bone biopsy
Symptoms Of Rickets
Rickets is described as the weakening and softening of bones, which is caused by prolonged lack of exposure to Vitamin D. Look out for the following rickets symptoms in your child to get quick and effective treatment.
1. Fragile bones
A symptom that is commonly associated with rickets and severe calcium and Vitamin D deficiency can lead to very weak bones, increasing the risk of fractures. Your child could have fragile bones, if they suffer from fractures frequently.
2. Pain in the spine and legs
Due to the bones being soft and weak, they become sore, making it very painful for a child. This might make your child reluctant to walk, so they may waddle and tire easily after a few steps.
3. Teeth problems
A child with rickets may show abnormalities in teeth structure, holes in the enamel, increasing cavities, and delay in teeth growth and formation.
Good dental care helps your children develop good dental habits. Read more about how to manage dental problems in children.
4. Skeletal deformities
When your child’s body has a deficiency in the required nutrients, rickets lead to many skeletal abnormalities. These include bowed legs or rickets leg, which refers to a curve in the spine, protruding breastbone, an oddly shaped skull, and pelvic deformities.
Nutritional rickets usually presents in infancy or preschool age, usually as widened wrists or bowing of legs.
5. Retarded growth and development
Delay in the development of bones and growth can lead to your child having short stature and stunted growth.
6. Craniotabes
This is a disorder where the bones of the skull are soft, and the fontanels are wide. This is frequently seen in infants who are older than three months.
7. Rachitic chest
In this case, a child is seen with a wide costochondral junction, which is the joint between the ribs, and Harrison’s groove, a depression at the lower side of the rib cage that develops when the diaphragm pulls the soft ribcage.
A condition known as rachitic rosary can result in the thickening caused by nodules forming on the costochondral joints. This appears as a visible bump in the middle of each rib in a line on each side of the body. This somewhat resembles a rosary, giving rise to its name.
8. Hypocalcemia
Defined as low calcium levels in the blood, infants with hypocalcemia may show signs and symptoms such as muscle spasms and convulsions.
Causes Of Rickets
Rickets is a bone disorder in children that leads to weak bones, muscle pain, and skeletal deformities. Today, nutritional rickets or rickets caused by the deficiency of Vitamin D, calcium, or phosphorus are the most common bone diseases affecting children. But other than this, rickets can be caused by genetics, drugs, or lack of mineralization.
These are the common types of rickets caused due to several deficiencies. These include:
1. Calcipenic rickets
This is the most common form of rickets, along with Vitamin D deficiency that is reported in children. This type of rickets develops due to a deficiency of calcium in the body. This can occur due to trouble in absorbing calcium seen in diseases such as celiac diseases.
2. Phosphopenic rickets
As the name suggests, this type of rickets is caused by the deficiency of phosphorus in your body. This can not only be due to low intake of phosphorus-rich food but also due to factors such as problems in phosphorus absorption by the intestine or high renal loss.
3. Vitamin D-dependent rickets
Vitamin D-dependent rickets is the most common type of rickets that children all over the world suffer from. This is the type of rickets caused by the deficiency of Vitamin D. This can be due to problems in the synthesis of Vitamin D, a defect in the Vitamin D receptor, low consumption of Vitamin D-rich food, and low exposure to sunlight.
4. Genetics
Other than the lack of nutrients in the body, rickets can also be genetic in nature. This is attributed to the genetic mutation of certain genes that stop the synthesis of Vitamin D in the body.
5. Familial hypophosphatemic rickets
This is the most commonly inherited form of refractory rickets, being inherited as X-linked dominant with variable penetrance. Sporadic instances are frequent and an autosomal recessive inheritance has also been reported. The gene responsible for X-linked hypophosphatemic rickets is termed as PHEX gene (phosphate regulating gene with homology to endopeptidases on the X chromosome)
6. Renal tubular acidosis (RTA)
Proximal or RTA are important causes of refractory rickets in children. The conditions are characterized by hyperchloremic metabolic acidosis with normal blood levels of urea and creatinine. Patients with proximal RTA may show low levels of phosphate, aminoaciduria (amino acids in the urine), and proteinuria (proteins in the urine). The use of bicarbonate and phosphate supplementation results in the healing of rickets.
7. Chronic kidney disease
Refractory rickets may occasionally be the presenting manifestation of chronic kidney disease. The features of the mineral bone disease depend on the patient's age and duration of disease. Elevated blood levels of creatinine, phosphate, and parathormone are characteristic. Therapy consists of restricting phosphate intake and providing supplements of calcium and active Vitamin D analogs.
8. Oncogenic rickets
Mesenchymal tumors may secrete fibroblast growth factors that result in phosphaturia (phosphates in urine), hypophosphatemia (low level of phosphorous), rickets, and muscle weakness.
9. Secondary to other diseases
-
McCune-Albright syndrome: It is a disorder in which the bones, skin and several hormone-producing (endocrine) tissues are affected.
-
Epidermal nevus syndrome: The presence of skin lesions known as epidermal nevi that are associated with additional extra-cutaneous abnormalities, affecting the brain, eye, and skeletal systems.
-
Dent's disease: It is a chronic kidney disorder that causes, kidney problems as a result of damage to the structures called proximal tubules.
Risk Factors For Rickets
There are certain factors that can make your child more vulnerable and at risk of developing rickets. They are:
-
People with dark skin are more prone to developing rickets due to high levels of the pigment melanin, which reduces the skin’s ability to produce Vitamin D from the sun.
-
Lack or low exposure to sunlight in colder regions of India.
-
Low consumption of food rich in Vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus.
-
Infants who are fed only breast milk, which has a low amount of Vitamin D.
-
Individuals who stay more indoors during the daylight hours.
Note: Our bodies produce more Vitamin D when they’re exposed to sunshine, so you’re more at risk for rickets if you live in an area with little sunlight.
Diagnosis Of Rickets
You must go to a pediatrician as the first point of contact. They will first conduct a physical examination to check for tenderness or pain in the bones by lightly pressing on them. During the examination, the doctor will gently press on your child's bones, checking for abnormalities. He or she will pay particular attention to your child's:
Skull: Babies who have rickets often have softer skull bones and might have a delay in the closure of the soft spots (fontanels).
Legs: While even healthy toddlers are a little bowlegged, exaggerated bowing of the legs is common with rickets.
Chest: Some children with rickets develop abnormalities in their rib cages, which can flatten and cause their breast bones to protrude.
Wrists and ankles: Children who have rickets often have wrists and ankles that are larger or thicker than normal.
Once that is done, your pediatrician may order certain tests to help make a definitive rickets diagnosis. These tests include:
-
Blood tests: These blood tests will be done to measure the levels of calcium, phosphorus, parathyroid hormone, and alkaline phosphatase (ALP) in your blood.
-
Urinary calcium: In the diagnosis of rickets, establishing an inappropriately high urinary calcium excretion in the face of low serum calcium levels is important.
-
Bone X-rays: X-rays will be conducted to check for any deformities in the bones.
-
Bone biopsy: In rare cases, if the situation demands it, a bone biopsy will be performed, which involves the removal of a small part of the bone, which is sent to a laboratory for analysis.
-
DEXA scan: Also known as bone densitometry, it is a means of measuring bone mineral density (BMD) using spectral imaging.
Prevention Of Rickets
Here are a few tips or suggestions that can go a long way in preventing the development of rickets. These include:
1. Sun exposure
The National Health Service of England suggests that exposing your hands and face to the sun every day can prove useful in preventing rickets. Don’t let your child in the sun for more than 60 minutes (depending on their skin type); if you do so, you must apply sunscreen to prevent sunburns. Also, reduce the amount of time of exposure to the sun between 10 AM to 4 PM as sun rays are intense during this period of time.
Here's more on how to choose the right sunscreen and the right way to use it.
2. Diet rich in phosphorus, calcium, and Vitamin D
Eating food filled with essential nutrients such as Vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus, is important for healthy bone development and growth. Different types of fish, meat, egg yolks, and mushrooms can also help your child to prevent acquiring Vitamin D deficiency. It is also suggested to add foods rich in calcium and phosphorus to the diet.
Exposure to ultraviolet B light (most easily obtained when the sun is highest in the sky), cod liver oil, halibut-liver oil, and viosterol are all sources of Vitamin D.
3. Vitamin D supplements
Adults, pregnant women, and children over the age of 1 year and older are suggested to take 10 mcg of Vitamin D supplements every day, while children at birth, up to 1 year old, can take 8.5 mcg to 10 mcg of Vitamin D tablets every day or 500 ml of infant formula every day.
Vitamin needs of the body are generally met through your diet, but Vitamin D is an exception. Read more about it.
Specialist To Visit
If your child has any signs or symptoms of rickets such as bone pain, delayed growth, muscle weakness, or skeletal problems, take them to your doctor for a check-up.
If you are an adult and are experiencing bone pain or muscle weakness, see your doctor to get it checked.
Specialists that can help in the treatment and management of rickets include:
-
Pediatrician
-
General physician
-
Orthopedic specialist
Take medical advice from world-class professionals if you notice any symptoms.
Treatment Of Rickets
For the treatment of rickets, a diet rich in Vitamin D, calcium, and phosphorus can help. Other treatment options include:
1. Surgery
Deformed bones due to rickets can be treated without surgery. However, in severe cases, surgery may be the only option to correct severely bowed legs, among other bone deformities. Chest or pelvic deformities and growth retardation may be permanent and can not be treated through surgery.
2. Stoss therapy
In this type of treatment, a single large dose of Vitamin D is administered orally or intramuscularly for infants less than a month old. Oral treatment is advised because it restores Vitamin D levels quickly. This regimen is generally both safe and effective in treating Vitamin D deficiency rickets.
3. Multiple doses of Vitamin D
In this regimen, small, daily doses of Vitamin D are given depending on the age of the child. The daily dose for infants less than a month old, 1-12 months, more than 12 months are 1000 IU, 1000 – 5000 IU, and 5000 IU, respectively, for a period of 2 to 3 months. Eventually, a dose of 400 IU is recommended for daily consumption.
4. Calcium and phosphate supplements
For rickets resulting from genetics, treatment by a pediatric endocrinologist and orthopedic specialist is suggested. For Vitamin D-dependent rickets, children are treated with high doses of calcitriol and calcium. If your child is diagnosed with familial hypophosphatemic rickets, oral administration of phosphate supplements along with Vitamin D is prescribed as treatment.
Home-care For Rickets
Doctors have pointed out that diet plays an incredibly important role in the prevention and treatment of rickets. Follow these steps to fight rickets:
-
You must give your child 400 IU/day of vitamin D supplementation to fight Vitamin D-dependent rickets.
-
If your child is still on breastmilk, completely or partially, 400 IU/day Vitamin D should be introduced into the diet until he/she starts receiving at least 1 liter of formula per day.
-
Your child should be given 400 IU/day of Vitamin D, if he/she is receiving less than 1 liter of formula per day and is not consuming mother’s milk.
-
Include foods such as milk, yogurt, cheese, meat, and fish to help increase the levels of Vitamin D, calcium and phosphorus levels.
-
If your child is lactose intolerant, you can give orange juice or soy milk as both contain high concentrations of Vitamin D.
When you hear calcium, all you can think of is a glass of milk. However, there’s much more to calcium than just milk and milk products. Read more about calcium-rich foods and supplements.
Complications Of Rickets
Rickets caused due to deficiency of calcium may lead to a child getting seizures, breathing problems, and cramps. But in the long run, it can lead to serious complications, including complications like:
-
Short stature
-
Multiple bone fractures
-
Pneumonia (lungs become filled with fluid)
-
Dental hypoplasia (poor formation of enamel))
-
Cardiomyopathy (disease of the heart muscle where the heart muscle is unable to pump enough blood to the muscle)
-
Hydrocephalus (fluid buildup in the cavities of the brain)
-
Seizures
-
Cavities in the teeth
-
Irregularities in the bones
Alternative Therapies For Rickets
Ayurveda has been treating various medical conditions for centuries, and many people have seen the effect of that. Find below a few ayurvedic remedies that can help in the treatment of rickets. Consult an Ayurvedic practitioner for proper guidance.
1. Pearl ash
Administer up to 125 mg of moti bhasma or pearl ash with two teaspoons of honey to your child twice a day. In case of a critical condition, consult an Ayurvedic practitioner.
2. Oatstraw bath
Take dried oatstraw herb and boil it in 4 liters of water and use it for bathing twice every week.
3. Dandelion tea
Dry dandelion leaves and add them to a cup of boiling water. Let the leaves sit for about 5 minutes. After 5 minutes, strain the water and serve the tea to your child.
4. Nettle herb
Add an ounce of dried nettle herb to a jar and pour one-quarter of hot water into it. Cover the jar and let it sit overnight. Strain the water and drink two cups daily.
5. Horsetail tea
Add one teaspoon of horsetail tea leaves to 2 cups of hot water along with oat straw herb. Let it steep for 5 to 7 minutes. Strain the water and drink the tea after every meal.
Living With Rickets
If your child has been diagnosed with rickets, you can follow these tips to effectively manage the disease:
-
Give Vitamin D supplements every day after consulting your doctor.
-
Make your child sit under the sun for 10-15 minutes (depending on their skin type) every day.
-
Give the child a diet that is rich in meat, fish, milk, and dairy products.
-
Make the child engage in any form of physical exercise every day to strengthen their bones.
-
Take your child to a qualified physiotherapist on a regular basis to ensure better pain management and mobility. It will help in managing rickets better.
If you see your child still suffering from muscle pain and cramps, please consult your doctor for further treatment. You should also take your child to a qualified physiotherapist who can help in improving physical functioning and pain management.
Doctors might suggest applying braces in some cases to ensure straighter longitudinal growth and provide support to limbs. Braces are also applied post-surgery. However, there is no valid study confirming the validity of bracing to treat or manage rickets. If your doctor advises bracing, make sure that your child wears braces properly and on a regular basis.
Rickets can be very painful for a child. While the symptoms may be severe and scary, they can be treated easily with the proper vigilance of the caregiver. Caregivers should ensure proper diet, physiotherapy, and outdoor activities for the child.
To get sufficient Vitamin D from sunlight, expose your back to the sun. Read about more ways to give your body the Vitamin D it needs.