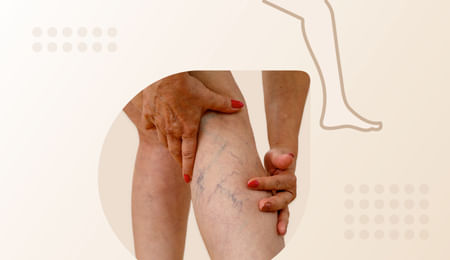
Varicose veins
Varicose veins are abnormal, dilated blood vessels caused by a weakening of the walls of the blood vessels. They may appear as swollen, twisted clusters of blue or purple veins. These occur because standing and walking increases the pressure in the veins of the lower body.
Varicose can appear anywhere, but most often appear on the legs, in the pelvic area, and on the surface of the skin. Mild cases of varicose veins just produce leg discomfort and may just look aesthetically unpleasing but the severe form can lead to pain, swelling, itching bleeding, and eventually ulcer formation.
Older women are at a higher risk of developing varicose veins due to hormonal changes and loss of elasticity of the vein walls. Other risk factors can include prolonged standing or sitting, family history, and trauma.
Treatment might involve conservative or surgical management. Conservative management comprises self-care measures and compression therapy. Surgical or minimally invasive procedures are done by a healthcare provider to close or remove veins.
- Adults above 55 years of age.
- Both men and women, but more common in women.
- Legs
- Feet
- Calves
- Pelvis
- Lymphedema
- Deep vein thrombosis
- Cellulitis
- Stasis dermatitis
- Tourniquet tests: Trendelberg test and Perthes test.
- Imaging tests: Venous doppler test, Color duplex ultrasound scan, Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and CT Angiogram.
-
Conservative management: Compression therapy.
- Surgical management: Conventional surgery, Vein stripping, Radiofrequency, and laser ablation.
- Minimally invasive procedures: Endovascular Laser Ablation( EVLA), Micropuncture or micro-incision or stab phlebectomy, and Transilluminated powered phlebectomy
- General physician
- Vascular surgeon
- Physical medicine rehabilitator
- Primary care provider
Symptoms Of Varicose Veins
Patients with varicose veins present with symptoms ranging from asymptomatic to significant symptoms, which include:
-
Discomfort
-
Itching (eczema)
-
Swelling
-
Aching pain that may get worse after sitting or standing for a long time
-
Blood clots in the deep veins of the legs
-
Twisted, swollen, and lumpy looking veins
-
The veins are blue or dark purple
-
Throbbing or cramping
-
Rash that is itchy or irritated
-
Darkening of the skin and loss of soft texture of the skin
-
A minor injury to the affected area may result in longer bleeding than normal
-
Tender areas around the veins
-
Fat under the skin just above the ankle can become hard, resulting in the skin shrinking
-
Irregular whitish patches that look like scars appear at the ankles
-
Irresistible urge to move the legs, typically in the evenings.
Varicose veins can lead to painful ulcerations on the legs if not managed properly. Learn how to effectively manage varicose veins.
Causes Of Varicose Veins
Varicose veins may be caused by weakened valves within the veins that result in the pooling of blood in the veins instead of traveling to the heart. The causes of varicose veins can include:
-
Primary varicose veins: These can have a hereditary factor like weakness in the wall of the vein and occur in some members of the same family.
-
Secondary varicose veins: These develop because of secondary causes such as trauma or deep vein thrombosis (blood clots in the deeper veins).
-
Familial and congenital varicose veins: These are due to disorders due to vascular malformation in the limb, present at birth.
Risk Factors For Varicose Veins
The most important risk factors leading to the development of varicose veins are:
Age
This is due to the loss of elasticity of the tissues as a person gets older, causing the valve system to fail.
Gender
Women have a higher incidence of varicose vein disease due to high levels of female hormones (estrogen) and their effect on the vein walls.
Family history
Studies show that screening of parents and family members revealed if parents and grandparents had the problem, it will increase the risk of varicose veins irrespective of gender.
Obesity
Being overweight can put extra pressure on veins, studies demonstrate that the risk increases especially in overweight women.
Know more about the 6 health risks of obesity.
Alcohol and smoking
Studies concluded that alcohol is likely to increase the risk of varicose veins in women and smokers had a higher incidence of varicose veins compared with non-smokers in both genders.
Are e-cigarettes safe? Do they help you quit smoking?
Get all these questions answered
Hormonal changes
These occur during different stages of life and include puberty, pregnancy, menopause, post-menopause, hormone replacement, and other medicines containing estrogen and progesterone that may contribute to the development of varicose veins.
Prolonged standing
Occupations that involve prolonged standing increase the volume and pressure of blood in the lower legs due to the effects of gravity leading to the development of varicose veins.
Immobility
Lack of mobility like sitting for a long time especially when legs are bent or crossed may force veins to work harder to pump blood to the heart increasing the risk of varicose veins formation.
Physical trauma
Trauma or damage to the underlying blood vessels is an important risk factor leading to the formation of varicose veins.
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT)
A DVT occurs when a blood clot forms in one or more of the deep veins in the body, especially in the legs. DVT significantly increases the risk of incidents of varicose veins.
Tall height
In both sexes, increasing height showed a significant relationship with varicose veins.
Know the actual reason why some people are taller than others.
Diagnosis Of Varicose Veins
Diagnosing varicose veins requires a thorough history, physical examination, and series of tests. They include:
Complete medical history
This should include previous interventions or surgery on the affected leg, pregnancy, ulcerations, trauma, any history of uterine fibroids and cancer, previous DVT (deep vein thrombosis), past hospital stays, cardiovascular disease, and previous lower limb fracture.
Clinical examination
The clinical evaluation of varicose veins in the standing position and inspected for redness,
tenderness, swelling, hyperpigmentation, and ulcerations. Classification of venous reflux is used to assess the clinical severity of symptoms, it includes:
C0: No visible or palpable signs of venous disease
C1: Reticular veins (purple blue veins)
C2: Varicose veins
C3: Edema (swelling)
C4a: Pigmentation and itching
C4b: Changes in the skin of the lower legs and White scar as a result of healed ulcer
C5: Healed leg ulcer
C6: Active ulcer on the leg
To determine the exact cause the tests include:
-
Trendelenberg test: Also known as Brodie–Trendelenburg test, it determines the competency of the valves in the superficial and deep veins of the legs in patients with varicose veins. It is done by elevating the leg to 45º, and a tourniquet is applied to the midthigh after the veins have completely drained.
-
Perthes test: This is done in a standing position with a tourniquet applied to the midthigh. If the varicose veins collapse after a 5-minute walk or varicose veins become more prominent and painful with walking, then the deep veins are obstructed.
Imaging techniques
If the cause of varicose veins is not clear from the clinical examination or if an intervention is being considered then imaging tests are done. They include:
-
Venography: It is a procedure of an x-ray of the veins after a special dye is injected into the bone marrow or veins. It is done to find blood clots, and identify a vein for use to assess varicose veins before surgery.
-
Venous doppler test: This is an ultrasound scan to check the direction of blood flow in the veins and check if there are any blood clots in the veins.
-
Color duplex ultrasound scan: It involves using high-frequency sound waves to look at the speed of blood flow, and the structure of the veins in the legs.
-
Computed tomography (CT): It can help find deep, hidden varicose veins and even the root cause behind the symptoms. Studies show that CT venography can provide an excellent road map for varicose veins surgery.
-
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI): It can be used as an alternative tool that plays a better role in assessing varicose veins of the lower extremities and deep veins of the pelvis and abdomen.
-
CT Angiogram: This test can help your doctor confirm whether you have varicose veins or any other problem. A dye is injected that outlines your veins on x-ray images.
Ambulatory venous pressure measurements
It is used to detect the decline in pressure from a higher value in the leg veins. Ambulatory venous pressure (AMVP) measurement is considered the gold standard in evaluating calf pump function in chronic venous disease.
Book your tests from the comfort of your home
Prevention Of Varicose Veins
As the saying goes” he who has a healthy body has everything” and the prevention of varicose veins mainly consist of making lifestyle changes that you would do just to keep yourself healthy. They are as follows:
Be active and exercise regularly
Regular exercise is a way to promote good blood circulation, as well as increase vein and
muscle strength. Strenuous exercises should be avoided if you already have varicose veins
Are you too lazy to sweat?
Read more about tips and tricks that can help you get moving.
Maintain a healthy weight
As obesity is one of the known factors for the emergence of varicose veins, weight control helps avoid pressure on leg circulation.
Avoid prolonged sitting or standing
If you must stand for a long time, shift weight from one leg to the other every few minutes. While sitting for a long period, take short walks every 30 minutes.
Note: Avoid high heels for a long time as this can result in lost efficiency of the veins causing pooling of venous blood in the leg. You can also buy heel supporters that can help you with the discomfort.
Explore our range now
Wear loose clothing
Extra tight clothes throughout the day can reduce blood circulation, so, be sure to wear loose-fitting comfortable clothing to help promote good circulation.
Keep your legs elevated
To improve blood circulation in your legs take several short breaks throughout the day to elevate your legs above the heart level.
Use compression stockings
Wearing compression stockings or socks improves blood flow by placing pressure on the legs relieving leg swelling and lowering the risk of blood clots formations in the legs.
Buy compression stockings online.
Eat the right diet
Excess salt can cause swelling in the legs. Eating a low-sodium diet with high-fiber foods can help to prevent varicose veins.
Control your blood pressure
High blood pressure puts an extra strain on blood vessels making them more susceptible to becoming varicose veins.
Limit sun exposure
Sun exposure can worsen the appearance of varicose veins and excessive exposure to the sun can cause spider veins (small dilated red or purple veins) on the cheeks or nose in fair-skinned people.
Protect yourself from the harsh rays of the sun. Choose from the widest range of sunscreens that best suit your skin.
Specialist To Visit
Varicose veins require accurate diagnosis and a comprehensive treatment team doctors who can help you manage them and they include:
-
General physician
-
Vascular surgeon
-
Physical medicine rehabilitator
-
Primary care provider
A vascular surgeon specializes in surgery for vascular system diseases. A physical medicine and rehabilitation doctor restores function and quality of life to those with physical disabilities and a primary care provider (PCP) prevents, diagnoses, and treats diseases.
When to visit your doctor?
Take an appointment with the doctor immediately if:
-
You have pain while walking or standing
-
You develop a sore or tender lump near a varicose vein
-
You have swelling in your ankles or feet
-
Your skin over a varicose vein bleeds on its own or when injured.
If you notice any of these symptoms seek advice from our trusted team of doctors immediately.
Treatment Of Varicose Veins
Varicose veins treatment requires a correct understanding of the severity of symptoms. The treatment consists of the following:
Conservative management
For individuals with milder symptoms and who do not want to undergo surgery using long-term graduated compression stockings, leg elevation, and oral pain medications can be a means to relieve the symptoms. Stockings should be worn daily if you want to see results and avoid surgery.
Surgical management
For patients with symptomatic veins and substantial venous incompetence, surgery has been the optimal treatment for many years. Traditional surgical treatment consisted of the following:
-
Conventional surgery: A small incision is made in the groin crease and the top of the main incompetent vein is dissected and tied off. A fine plastic wire is passed through the vein and retrieved through the inside of the leg at the knee level.
-
Vein stripping: This procedure is used to remove or tie off a large vein in the leg that helps treat varicose veins.
-
Radiofrequency and laser ablation: These involve passing a probe up the long vein from knee level to the groin under ultrasound guidance and then ablating the vein in sections. This avoids a groin incision and may lead to less bruising and quicker recovery.
-
Sclerotherapy: This involves the injection of an agent called sclerosant into varicosities, followed by a period of compression bandaging and/or compression hosiery. The main risk of sclerotherapy is injection outside the vein, which can result in local tissue necrosis and scarring.
-
Foam sclerotherapy: This involves mixing sclerosant with a small quantity of air to produce a foam that spreads rapidly and widely through the veins, pushing the blood aside and causing the veins to go into spasm.
Minimally invasive procedures
-
Endovascular Laser Ablation( EVLA): This is a preferable treatment usually for larger varicose veins in which a thin catheter inserted into an enlarged vein heats the tip of the catheter using radiofrequency energy. As the catheter is pulled out, the heat destroys the vein by causing it to collapse and shut.
-
Micropuncture or micro-incision or stab phlebectomy: In this procedure, a physician makes a tiny incision and uses a surgical instrument or a large needle to hook the problem vein through the opening. The vein is then removed a tiny piece at a time.
-
Transilluminated powered phlebectomy: The procedure involves inserting a light under the skin while simultaneously injecting a mixture of saline and a local anesthetic that guides the surgeon to cut the vein into smaller pieces and suction the pieces from the space.
Management of spider veins
Many patients will have visible superficial veins referred to as "spider veins". These may not be a cause of worry just for cosmetic sake but can also be painful. Its management includes:
-
Liquid sclerotherapy: It involves the injection of a liquid sclerosant into the superficial veins.
-
Phlebectomy: It involves removing larger superficial varicose veins through small 2 mm to 3 mm incisions.
-
Laser therapy: Laser light can destroy the vein without damaging your skin. Laser therapy is only used to treat spider veins and is not useful for varicose veins.
Home care For Varicose Veins
Lifestyle modification is crucial to ensure as complete and durable a treatment response as possible. All management modalities to treat varicose veins are considered safe and can be long-term or short-term. But, do we always have to opt for surgery? there are certain home remedies that can be beneficial, but they include:
1. Apple cider vinegar: It helps clean the body and enhances the circulation of blood through the veins. A study suggested that the external application of apple vinegar on varicosity patients increased the positive effects of conservative treatment.
Explore our range of apple cider vinegar products.
2. Red chili (Laalmirch): Also known as cayenne pepper is rich in vitamin C and antioxidants that treat allergies and viruses. The substance inside the pepper prevents blood clotting, helping prevent varicose veins.
3. Garlic (Lahsun): It contains flavonoids that help strengthen the veins and blood vessels, keeping them safe from damage thus, reducing varicose veins.
4. Lemon (Nimbu): It is a powerhouse of nutrients and minerals and vitamin C that can prevent varicose veins, and fluctuating blood pressures, and keeps the skin glowing too.
Note: Extract the juice from 2 to 3 lemons and add 4 teaspoons of olive oil. Mix it with the garlic paste and leave it overnight. Massage the affected area of Varicose veins with that mixture twice a day for two months to see the results. Read more about the health benefits of lemons.
Complications Of Varicose Veins
Varicose veins complications might be rare, but they include:
-
Venous ulcers: These are leg ulcers caused by problems with blood flow in your leg veins.
-
Pain: An achy or heavy feeling in the legs along with burning, throbbing, muscle cramping, and swelling in the lower legs.
-
Poor cosmesis: Cosmesis usually refers to the surgical correction of disfiguring defects, which becomes difficult with the presence of varicose veins.
-
Thrombophlebitis: Swelling of the veins in your leg.
-
Deep vein thrombosis (DVT): It can cause pain and swelling in the leg, and may lead to serious complications like pulmonary embolism.
-
Bleeding: Uncontrolled bleeding near the surface of your skin can result from varicose veins.
Alternative Therapies For Varicose Veins
Alternative or complementary therapies have proven to alleviate the symptoms of varicose veins and when incorporated with the treatment plan have shown promising results. Some of them include:
Hydrotherapy
Studies show that hydrotherapy is effective in treating primary varicose veins along with compression therapy and other conservative treatments. The warm sitz bath hydrotherapy is an effective non-invasive therapy for uncomplicated varicose veins and requires a high degree of patient compliance.
Leech therapy
A study suggested that the medicinal leech sucks venous blood and aids ulcer healing, and can be used as an effective adjunct in the management of complicated varicose veins. This however requires further evaluation by controlled trials.
Ayurveda
It can be helpful in treating painful venous ulcers, a complication of varicose veins. Studies suggest that therapeutic procedures, sodhana (purification therapy), act on non-healing ulcers and help them heal.
Living With Varicose Veins
Varicose veins cannot always be avoided completely, they may cause serious issues if not taken care of. Some pieces of advice that can help you in order for the disease, not to progress include:
Make the right dietary choices
Potassium-high foods, such as almonds and pistachio nuts, reduces water retention and can help in reducing varicose veins. Also, cutting down on salty food can minimize water retention.
Know more about the top 50 potassium-rich Indian food sources.
Add flavonoids to your plate
Flavonoids improve blood circulation, reduce blood pressure in the arteries, and can relax blood vessels, all of which can reduce varicose veins. Foods that contain flavonoids include:
Massage religiously
Gently massaging the affected areas can blood circulation through the veins. Use massage oils or moisturizers for optimal effects and avoid pressing directly onto the veins as it can damage fragile tissues.
Make sure to keep moving
Avoid sitting for long periods of time and aim to get up and move around or change position frequently to keep the blood flowing smoothly. Also, avoid sitting with crossed legs, as it restricts blood flow to the legs and feet, which may add to circulation problems.
Take a cold shower
Cold water improves blood circulation. You can also massage with a jet of water from the feet to the thighs. Make sure to keep the skin of the affected area clean and well-hydrated.
Say “No” to alcohol and tobacco
As we have established these are the risk factors for varicose veins, they can worsen the symptoms if you already have varicose veins, hence avoiding them will not only help you with the symptoms but it can help you take that extra step towards leading a healthy life.
Try our smoking cessation range if you are keen on quitting this deadly habit.
Be aware of the tourist class syndrome
Also known as traveler's thrombosis is a condition that occurs when you have to sit in the same position for a long time. To avoid this, perform foot exercises, keep sipping water, wear loose comfortable clothing, and make sure to keep moving every 2 hours in case of a long flight.
Take post-procedure follow-ups seriously
After endovenous ablation treatment, most physicians recommend a duplex ultrasound examination of the treated leg within the first week to evaluate for deep vein thrombosis.