Want to know more?
Read Our Editorial PolicyHave issue with the content?
Report Problem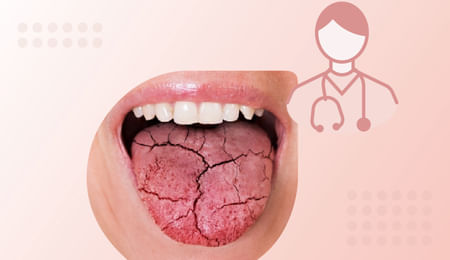
Xerostomia
Also known as Dry Mouth, Xerotos and WaterlessnessOverview
Xerostomia, commonly known as dry mouth, is a condition in which the person’s salivary glands don't make enough saliva to keep the mouth wet. It is generally seen as a side-effect of certain medications, symptom of some medical disorders or as an adverse effect of radiation in cancer therapy. Rarely, the cause may be directly related to the salivary gland itself.
Saliva helps prevent tooth decay by neutralizing acids produced by bacteria, limiting bacterial growth, and washing away food particles. Saliva also enhances the ability to taste and makes it easier to chew and swallow food. Along with this, saliva contains enzymes that help in the easy digestion of food.
Decreased salivary secretion can range from minor discomfort to something that affects general wellbeing and the health of your teeth, gums, and surrounding oral tissues. Identifying the factors and causes for xerostomia creates a path for the treatment.
Key Facts
- Adults above 50 years of age
- Both men and women but more common in women
- Oral cavity (mouth)
- Hyposalivation
- Sialometry
- Saliograpy
- Salivary scintigraphy
- Biopsy
- Blood tests: Complete blood count (CBC), Blood sugar tests & Electrolyte levels
- Saliva substitutes
- Saliva stimulants
- Medications: Pilocarpine & Cevimeline
- Other medications and preparations: Anethole trithione, Yohimbine & Human interferon alfa (IFN-a)
- Dentist
- General physician
Symptoms Of Xerostomia
Xerostomia is generally the symptom for many health conditions and a side-effect of certain medications. But it can present itself with other symptoms that include:
-
Changes in perceiving the tastes along with intolerance to spicy, salty, or sour foods or drinks
-
Burning sensation in the mouth in addition to sticky, dry, and rough tongue
-
Difficulty in chewing, swallowing, tasting, or speaking
-
Sore throat
-
Atrophic, cracked, or chapped lips besides peeling
-
Mouth ulcers or sores
-
Increased chances of infections in the mouth
-
Hoarseness of the voice
-
Bad breath or halitosis
-
Increased dental cavities or decay
-
Ineffectiveness to retain dental dentures or any other oral prosthesis
Causes Of Xerostomia
Xerostomia is a condition when the salivary glands produce less saliva leading to dry mouth. Some of the common causes include the following:
1. Medications: This is the most common cause of xerostomia. Many medications that are sold over-the-counter mention dry mouth as the side-effect. Some medicines that are known to cause xerostomia are:
-
Medications for anxiety and depression
-
Drugs like anticholinergics that are used in the treatment of urinary incontinence, overactive bladder, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disorder
-
Decongestants and antihistamines used in allergies and cold
-
Some pain medicines
-
Some drugs are used in the treatment of high blood pressure
-
Certain bronchodilators used to treat asthma
-
Some medicines used in treatment of diarrhea
-
Certain muscle relaxants
-
Medications for Parkinson's disease
-
Drugs used in chemotherapy for the treatment of cancer
2. Radiation therapy: Radiation treatments to the head and neck region for treatment of cancer can cause irreversible damage to the salivary glands. This can lead to a significant decrease in salivary production.
3. Dehydration: Dehydration occurs when the body loses a lot of fluids without getting replenished. This can happen during hot summer months or conditions like vomiting, diarrhea, fever, excessive sweating, blood loss, or burns. When the body is dehydrated, production of saliva is reduced leading to dry mouth.
4. Mouth-breathing or snoring: Breathing through the mouth due to nasal congestion or snoring while sleeping causes saliva to evaporate. This leads to dryness in the mouth.
5. Medical conditions: Xerostomia can be a sign of medical conditions like:
-
Sjogren’s disease (formerly known as Sjogren syndrome)
-
Acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS)
-
Poorly controlled diabetes
-
Uncontrolled hypertension (high blood pressure)
-
Anemia
-
Sleep apnea
-
Cystic fibrosis
-
Mumps
-
Yeast infections
-
Rheumatoid arthritis
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
-
Parkinson's disease
-
Alzheimer's disease
-
Hepatitis C
-
Lymphoma
-
Chronic graft-versus-host disease seen in bone marrow transplant recipients
-
Salivary gland agenesis or aplasia
6. Aging: People might experience xerostomia as they age. The factors contributing to it can be the use of certain medications, changes in the body's ability to process medication, inadequate or improper nutrition, or long-term health problems.
7. Nerve damage: Any injury, infection, or surgery that causes damage to the nerves of the head or the neck region can result in xerostomia.
8. Smoking and drinking: Alcohol acts as a diuretic, meaning, as the body breaks down alcohol, it removes the water from the blood through urine. Also, smoking reduces the salivary flow rate leading to dryness of the mouth or xerostomia.
9. Use of recreational drugs: “Meth mouth” is a condition due to the use of methamphetamine that causes severe xerostomia and damage to teeth. Other drugs such as marijuana also can cause xerostomia.
10. Stress and anxiety: Cortisol (also called the stress hormone) is produced in excess when a person is under stress or is anxious. Increased levels of cortisol in saliva can change the composition of the saliva causing the mouth to become dry.
Risk Factors For Xerostomia
Xerostomia can be a symptom of an underlying condition or an adverse effect of certain medications. It can be permanent or temporary depending on the cause. Some of the risk factors associated with xerostomia are:
-
Medications like antidepressants and anxiolytics (anti-anxiety)
-
Autoimmune conditions like Sjogren’s disease and AIDS
-
Old age
-
Bulimia or anorexia
-
Blockage of major salivary duct such as from a salivary stone or infection
-
Smoking
-
Chemotherapy and radiation to the head and neck
-
Mouth breathing
-
Patients with mental or nervous disorders
-
Individuals wearing dentures
-
Pregnancy or breastfeeding
Diagnosis Of Xerostomia
The diagnosis of xerostomia is based on detailed:
Medical history
Details about duration, frequency, and severity of dry mouth are documented. The history of dryness at other sites (eyes, nose, throat, skin & vagina) along with complete prescription drug history, health conditions, and any other symptoms along with it are obtained.
Physical examination
Major salivary glands are examined for the presence of any pain, firmness, or enlargement. The amount and quality of saliva coming from the ducts inside the mouth is assessed.
Examination of the mouth
-
There may be very little or no pooled saliva on the floor of the mouth. The saliva may appear stringy, ropy, or foamy.
-
The presence of dry, sticky or reddish oral mucosa is inspected. Occasionally, fungal or yeast infections will be present, appearing as removable white plaques on the inner mucosal surface of the mouth.
-
Tongue may appear dry with decreased numbers of papillae.
-
The extent and pattern of dental decay is evaluated. Multiple dental caries, especially at the neck of the teeth or the tips of the teeth along with plaque accumulation, gum infections can be seen.
Several office tests and techniques can be utilized to detect the abnormal functioning of the salivary glands. These tests are as follows:
1. Sialometry
Also known as salivary flow measurement, it is a simple test or procedure that measures the flow rate of saliva. In this test, collection devices are placed over the parotid gland or the submandibular/sublingual salivary gland at the opening of the duct, and saliva is stimulated with citric acid.
The normal salivary flow rate for the parotid gland when it is not stimulated is 0.4 to 1.5 mL/min/gland. The normal flow rate for “resting” the whole saliva is 0.3 to 0.5 mL/min; for stimulated saliva, 1 to 2 mL/min. Values less than 0.1 mL/min are generally considered xerostomic.
2. Saliograpy
It is an imaging technique that may be used to detect any masses or stones in the salivary gland. It involves the injection of radio-opaque dye into the salivary glands.
3. Salivary scintigraphy
It can be useful in assessing salivary gland function. Technetium-99m sodium pertechnate is injected intravenously to ascertain the rate and density of uptake and the time of excretion in the mouth.
4. Biopsy
Minor salivary gland biopsy is often used in the diagnosis of Sjögren’s syndrome (SS), HIV-salivary gland disease, sarcoidosis, amyloidosis, and graft-versus-host disease (GVHD). Biopsy of major salivary glands is an option when malignancy (cancer) is suspected.
5. Blood tests
In addition to accessing the salivary glands, some blood tests may also help in detecting any underlying infection or disease. The tests are:
Prevention Of Xerostomia
Though xerostomia is quite common, it can often be prevented. Here are a few tips to prevent it:
-
Drink a minimum of 2L (i.e. 8 glasses of 250ml each) of water a day.
-
Start using a humidifier in your home, especially in the bedroom.
-
Breathe through the nose rather than through the mouth.
-
Consult the physician before taking any over-the-counter medications such as antihistamines and decongestants.
-
Avoid caffeinated beverages, tobacco, and alcohol, all of which increase dryness in the mouth.
-
Do not consume any recreational drugs as they may cause severe xerostomia.
-
Try maintaining and monitoring blood sugar levels in case of diabetes.
-
Practice good oral hygiene practices.
Note: If someone has to undergo radiotherapy, surgical transfer of one submandibular salivary gland to the submental space (deep compartment of the head and neck that lies in the midline below the chin) shields the gland during radiation therapy. Studies confirm that there is no adverse effect on the function of the gland in this position.
Specialist To Visit
Xerostomia is a disorder of the mouth. Though it may not appear to be serious, it can be an indicator of several underlying diseases or conditions. Severe xerostomia can cause difficulty in talking, swallowing, and eating food. It can hamper your self-esteem and confidence due to bad breath. Specialists to visit are:
- Dentists
- General physician
If you are facing such an issue, seek advice from our professionals.
Treatment Of Xerostomia
Xerostomia can be managed by several over-the-counter medications and products that aid in providing relief from the symptoms. These medications range from salivary substitutes and stimulants to products designed to minimize dental problems. They are as follows:
1. Saliva substitutes
These can be used as artificial saliva that help replace the lost moisture and lubricate the mouth. These substitutes are available commercially, but they can also be compounded. Artificial salivas do not stimulate salivary gland production but are designed to mimic natural saliva. Thus, they are considered as replacement therapy rather than a cure.
These salivary substitutes are available commercially as solutions, sprays, gels, and lozenges. In general, they contain an agent to increase viscosity such as carboxymethylcellulose or hydroxyethylcellulose, minerals such as calcium and phosphate ions and fluoride, preservatives such as methylparaben or propylparaben, and flavoring and related agents.
2. Saliva stimulants
A recently developed product called natrol dry mouth relief, which has a patented pharmaceutical grade of anhydrous crystalline maltose (ACM) is used to stimulate saliva production. It has been used in a clinical study of patients with Sjogren's syndrome and ACM was shown to increase secretions. Natrol dry mouth relief is formulated as lozenges that can be dissolved in the mouth three times daily. As its effect is to stimulate salivary glands, it is not recommended for patients whose salivary gland function has been lost through radiation therapy.
3. Medications
Pilocarpine: Pilocarpine is a muscarinic (M3) agonist which stimulates the secretion of saliva. It is indicated for the treatment of symptoms of xerostomia due to salivary gland hypofunction caused by Sjogren’s syndrome or by radiotherapy for cancer of the head and neck area.
Cevimeline: Cevimeline is a cholinergic agonist with a high affinity towards the muscarinic M3 receptors located on lacrimal and salivary gland epithelium, leading to an increase in the secretions of the exocrine glands. It is used to relieve the symptoms of xerostomia in patients with Sjogren’s syndrome.
Note: These prescription medications have to be avoided in patients having asthma & glaucoma.
4. Other medications and preparations
The following medications are under clinical trial and the efficacy is yet to be determined.
-
Anethole trithione: This is a bile secretion-stimulating drug or cholagogue. It acts by stimulating the parasympathetic nervous system and increases the secretion of acetylcholine, resulting in the stimulation of salivation.
-
Yohimbine: It is an alpha-2 adrenergic antagonist which indirectly results in an increase of cholinergic activity peripherally thus improving salivation.
-
Human interferon alfa (IFN-a): This drug is currently undergoing clinical trials to determine the safety and efficacy of low-dose lozenges in the treatment of xerostomia in patients with Sjogren’s syndrome.
Home-care For Xerostomia
Home remedies for xerostomia help in managing the symptom and provide relief however, these cannot be considered as the cure for it.
1. Try over-the-counter saliva substitutes or oral lubricants
Many different brands of salivary substitutes or oral lubricants are available in the market. They do not cure xerostomia but provide some relief and help during eating and speaking.
2. Drink a lot of water
Sipping water and staying hydrated can help relieve the symptoms and discomfort caused by xerostomia. Studies have shown that dehydration may be a causative factor in xerostomia and increasing the water intake can help treat mild dehydration.
3. Avoid certain medications
The most common cause for xerostomia is the use of certain medications. Talk to the doctor and understand if the medications are causing dryness in the mouth. Do not stop those medications abruptly without consulting the doctor.
The types of medicines that may cause dry mouth include:
-
Antianxiety medicines
-
Anticonvulsants
-
Antidepressants
-
Antihistamines
-
Antipsychotics
-
Sedatives
-
Smoking-cessation agents
-
Urinary incontinence agents
-
Bronchodilators
-
Decongestants
-
Diuretics
-
High blood pressure medications
-
Muscle relaxants
-
Narcotic analgesics
-
Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs
-
Opioid analgesics
-
Parkinson’s disease medications
4. Say no to dehydrating habits
Some of the common ways to prevent dehydration & thereby xerostomia are:
-
Quit smoking
-
Avoid caffeine
-
Limit alcohol use
-
Decrease sugar intake
5. Give importance to overall oral care
Xerostomia can be both a symptom and a cause of poor oral hygiene. Maintaining good oral hygiene plays a crucial role in the management of xerostomia. This includes frequent flossing, fluoride toothpaste use, and use of mouthwash.
When choosing a mouthwash, make sure it doesn't contain any alcohol as alcohol-based mouthwashes will only further increase dryness of the mouth. Also, mouthwashes containing xylitol can also help prevent dental caries.
Since dry mouth often leads to the development of fungal infections like oral candidiasis, antifungal mouth rinses, and dissolving tablets might be required. Dentures often lodge fungal infections, so they should be soaked daily in a chlorhexidine solution.
6. Try sugarless candies or gums
Sucking on sugar-free candies or products like chewing gums, cough drops, and lozenges may provide some short-term relief from xerostomia. Citrus, cinnamon or mint-flavored candies make good choices. Some sugarless gums and candies also contain xylitol which can help in prevention of dental cavities.
7. Use lip balms frequently
Moisturizing the lips with a lip balm or petroleum jelly every 2 hours can also be helpful.
8. Dietary modifications
Moisten foods with gravy, soups, sauces, creams, ghee or butter. Also. taking sips of water or fluids while having a meal can help in softening the food and chewing. Try to have foods that are at room temperature.
Restrict salty foods and dry foods like toast, cookies, dry breads, dry meats, dried fruits, and bananas. Foods and beverages with high sugar content should also be avoided.
9. Avoid mouth breathing consciously
Mouth-breathing can make xerostomia worse and may also cause other oral health problems.
10. Use a humidifier
Creating a humid environment may help in relieving xerostomia simply by adding more moisture to the surroundings.
Complications Of Xerostomia
Xerostomia can often be a contributing factor for both minor and serious health problems. It can affect nutrition and dental as well as psychological health. Some of the common problems associated with xerostomia include:
-
Constant sore throat
-
Burning sensation in the mouth
-
Halitosis or bad breath
-
Difficulty speaking and swallowing
-
Hoarseness of voice
-
Dry nasal passages
-
Excessive plaque accumulation
-
Gum diseases
-
Dental caries
-
Oral candidiasis
Alternative Therapies For Xerostomia
1. Home remedies
Herbal medicines have shown potentially good results on improving salivary function and to reduce the severity of xerostomia. Moreover, they are relatively safe. Some of the herbs that can be used to manage xerostomia are:
-
Aloe vera: The gel or juice inside the aloe vera plant is very moisturizing. Drinking aloe vera juice can be a treat to the mouth and provide relief from xerostomia.
-
Ginger: Ginger is known to help stimulate salivary production.
-
Homemade mouthwash: Blend 1 cup of warm water with 1/4 teaspoon of baking soda and 1/8 teaspoon of salt. Rinse your mouth for a few seconds then rinse with water. Repeat every 3 to 4 hours.
2. Oil pulling
Oil pulling is an old age ayurvedic technique of holding a few tablespoons of coconut or sesame oil in the mouth for 10 to 15 minutes without swallowing. Since the oil cleans out the mouth while coating and soothing irritated spots, it can give some relief in xerostomia.
3. Unani therapy
According to Unani therapies, the best way to manage xerostomia is through lifestyle modifications. This is based on Setteh-e-Zarurieah, which means consuming foods that are moisturizing in nature like rice cooked with milk, fresh fish, goat meat, foods that are prepared with pumpkin and spinach as well as purslane.
The best food for patients with xerostomia are almonds, figs, grapes, peaches, and fresh broad beans.
4. Acupuncture
In acupuncture, an acupuncturist inserts thin, disposable needles into the skin in such a way that energy flow increases to the mouth and throat. However, acupuncture as a therapy needs more studies and scientific backing.
Living With Xerostomia
Xerostomia is a condition that causes dryness of the mouth. It can be mild or severe depending on the cause. Xerostomia can be treated with salivary substitutes, salivary stimulants, and meditations.
In addition to these, the symptoms of xerostomia can be managed by following certain simple tips. They are as follows:
-
Drink at least 8 glasses of water everyday
-
Avoid medications that cause dry mouth
-
Try sugarless candies or gums
-
Limit the intake of caffeine and alcohol
-
Decrease the sugar intake
-
Maintain a good oral hygiene regimen
-
Use a non-alcohol based mouthwash
-
Try over-the-counter saliva substitutes or oral lubricants
-
Moisturize lips with a lip balm
-
Eat food with creams, ghee or butter
-
Restrict eating salty and dry food items
-
Avoid breathing through the mouth continuously
-
Use a humidifier in the house
-
Quit smoking
-
Get proper sleep
-
Avoid walking in the sun or excessive exercise
Furthermore, patients with xerostomia should avoid stresses such as anger, sorrow, and excessive fear. If the symptoms still persist consult a dentist or a physician to understand the root cause and manage the symptoms.
Frequently Asked Questions
References
- Villa A, Connell CL, Abati S. Diagnosis and management of xerostomia and hyposalivation. Ther Clin Risk Manag. 2014 Dec.
- Rad M, Kakoie S, Niliye Brojeni F, Pourdamghan N. Effect of Long-term Smoking on Whole-mouth Salivary Flow Rate and Oral Health. J Dent Res Dent Clin Dent Prospects. 2010 Fall;4(4):110-4. doi: 10.5681/joddd.2010.028. Epub 2010 Dec 21.
- Villa A, Abati S. Risk factors and symptoms associated with xerostomia: a cross-sectional study. Aust Dent J. 2011 Sep.
- Lisa Simon and Hugh Silk, ed. Diseases of the Mouth. Conn's Current Therapy 2021 (1st ed.). Elsevier; 2021. p 1029-1034.
- Helping Patients with Xerostomia. Xerostomia.
- Home Treatment. Dry mouth: Home treatment and prevention. October 2020.
- Heydarirad G, Choopani R. “Dry Mouth” From the Perspective of Traditional Persian Medicine and Comparison with Current Management. Journal of Evidence-Based Complementary & Alternative Medicine. April 2015:137-142.
- Tsuchiya H. Characterization and Pathogenic Speculation of Xerostomia Associated with COVID-19: A Narrative Review. Dentistry Journal. 2021.
- Abdullah MJ. Prevalence of xerostomia in patients attending Shorish dental speciality in Sulaimani city. J Clin Exp Dent. 2015 Feb 1.
- Wiener RC, Wu B, Crout R, Wiener M, Plassman B, Kao E, McNeil D. Hyposalivation and xerostomia in dentate older adults. J Am Dent Assoc. 2010 Mar.