- TOP CITIES
- New Delhi
- Gurgaon
- Pune
- Mumbai
- Bengaluru
- Kolkata
- Hyderabad
- Ahmedabad
- Chennai
- Indore
- Lucknow
- Jaipur
- Chandigarh
- Bhopal
- Noida
- Navi Mumbai
- Surat
- Patna
- Ludhiana
- Bhubaneshwar
- ALL CITIES
- Abohar
- Adilabad
- Adoni
- Agar
- Agartala
- Agra
- Ahmedabad
- Ahmednagar
- Aizawl
- Ajmer
- Akola
- Alappuzha
- Aligarh
- Alipurduar
- Alirajpur
- Allahabad
- Almora
- Alwar
- Ambala
- Ambattur
- Ambedkar Nagar
- Amravati
- Amreli
- Amritsar
- Amroha
- Anand
- Anantapur
- Ananthnag
- Anantnag
- Angamally
- Angul
- Ankleshwar
- Annur
- Anuppur
- Arakkonam
- Arambag
- Arantangi
- Araria
- Arcot
- Ariyalur
- Arwal
- Asansol
- Ashok Nagar
- Assaudh
- Attuvampatti
- Auraiya
- Aurangabad Bihar
- Aurangabad Maharashtra
- Aviyur
- Ayyangarkulam
- Azamgarh
- Badlapur
- Bagalkot
- Bageshwar
- Baghpat
- Bagpat
- Bahadurgarh
- Bahraich
- Baksa
- Balaghat
- Balangir
- Baleswar
- Ballia
- Bally
- Balrampur
- Banaskantha
- Banda
- Bangalore
- Bangalore Rural
- Banka
- Bankura
- Banswara
- Barabanki
- Baramati
- Baramulla
- Baran
- Baraut
- Bardhaman
- Bareilly
- Bargarh
- Barmer
- Barnala
- Barpeta
- Barrackpore
- Baruipur
- Barwani
- Basirhat
- Bastar
- Basti
- Bathinda
- Beawar
- Beed
- Begumganj
- Begusarai
- Behraghora
- Behrampur
- Belgaum
- Bellary
- Belur
- Bengaluru
- Betul
- Betul Ganj
- Bhadrak
- Bhadravati Karnataka
- Bhagalpur
- Bhandara
- Bharatpur
- Bharuch
- Bhatkal
- Bhavani
- Bhavnagar
- Bhilai
- Bhilwara
- Bhind
- Bhiwadi
- Bhiwandi
- Bhiwani
- Bhojpur
- Bhopal
- Bhubaneshwar
- Bhuna
- Bhusawal
- Bidar
- Bijapur Chattisgarh
- Bijapur Karnataka
- Bijnor
- Bikaner
- Bilaspur Chattisgarh
- Bilaspur Himachal Pradesh
- Birbhum
- Bishnupur
- Boisar
- Bokaro
- Bongaigaon
- Bongaon
- Botad
- Boudh
- Budaun
- Budgam
- Bukkapatnam
- Bulandshahr
- Buldana
- Buldhana
- Bundi
- Burdwan
- Burhanpur
- Buxar
- Cachar
- Calicut
- Chamarajanagar
- Chamba
- Chamoli
- Champawat
- Champhai
- Chandauli
- Chandel
- Chandigarh
- Chandrapur
- Changanassery
- Changlang
- Chatra
- Chennai
- Chhatarpur
- Chhindwara
- Chikkaballapur
- Chikkaballapura
- Chikmagalur
- Chintamani
- Chitradurga
- Chitrakoot
- Chittoor
- Chittorgarh
- Chrompet
- Churachandpur
- Churu
- Cochin
- Coimbatore
- Cooch Behar
- Cuddalore
- Cuddapah
- Cuttack
- Dadra & Nagar Haveli
- Dahanu
- Dahod
- Dakshina Kannada
- Daman
- Damoh
- Dantewada
- Darbhanga
- Darjiling
- Darrang
- Datia
- Dausa
- Davangere
- Debagarh
- Dehradun
- Delhi
- Deoghar
- Deoria
- Dera Bassi
- Devanahalli
- Dewas
- Dhakaoli
- Dhalai
- Dhamtari
- Dhanbad
- Dhar
- Dharmapuri
- Dharwad
- Dhemaji
- Dhenkanal
- Dholpur
- Dhone
- Dhubri
- Dhule
- Dhully
- Dibang Valley
- Dibrugarh
- Dibrugarh Tamil Nadu
- Dimapur
- Dindigul
- Dindori
- Dispur
- Diu
- Doda
- Dombivli
- Dombivli Station
- Dumka
- Dungarpur
- Durg
- Durgapur
- East Champaran
- East Garo Hills
- East Godavari
- East Kameng
- East Khasi Hills
- East Midnapore
- East Nimar
- East Siang
- East Sikkim
- East Singhbhum
- Ellanaickenpatti
- Ernakulam
- Erode
- Etah
- Etawah
- Faizabad
- Faridabad
- Faridkot
- Farrukhabad
- Fatehabad
- Fatehgarh Sahib
- Fatehpur
- Fazilka
- Firozabad
- Firozpur
- Gadag
- Gadarwara
- Gadchiroli
- Gajapati
- Gandhinagar
- Ganganagar
- Gangtok
- Ganjam
- Garhwa
- Gariaband
- Gautam Buddha Nagar
- Gaya
- Ghaziabad
- Ghazipur
- Gir Somnath
- Giridh
- Goa
- Goalpara
- Gobichettipalayam
- Godda
- Golaghat
- Golaniya
- Gonda
- Gondia
- Gopalganj
- Gorakhpur
- Greater Noida
- Greater Thane
- Gulbarga
- Gumla
- Guna
- Guntur
- Gurdaspur
- Gurgaon
- Guwahati
- Gwalior
- Hailakandi
- Halol
- Hamirpur Himachal Pradesh
- Hamirpur Uttar Pradesh
- Hansi
- Hanumangarh
- Hapur
- Harapanahalli
- Harda
- Hardoi
- Haridwar
- Hassan
- Hathras
- Haveri
- Hazaribag
- Hazaribagh
- Hinauti
- Hindaun
- Hingoli
- Hisar
- Hojai
- Hooghly
- Hosakote
- Hoshangabad
- Hoshiarpur
- Hoskote
- Hospet
- Hosur
- Howrah
- Hubli
- Hyderabad
- Ichalkaranji
- Idukki
- Imphal
- Imphal East
- Imphal West
- Indore
- Itanagar
- Jabalpur
- Jagatsinghapur
- Jaintia Hills
- Jaipur
- Jaisalmer
- Jajapur
- Jalandhar
- Jalaun
- Jalgaon
- Jallipatti
- Jalna
- Jalore
- Jalpaiguri
- Jammu
- Jamnagar
- Jamshedpur
- Jamtara
- Jamui
- Janjgir-Champa
- Jashpur
- Jaunpur
- Jayamala
- Jehanabad
- Jhabua
- Jhajjar
- Jhalawar
- Jhansi
- Jhargram
- Jharsuguda
- Jhujhunu
- Jind
- Jodhpur
- Jorhat
- Junagadh
- Jyotiba Phule Nagar
- Kachchh
- Kadamakkudy
- Kadapa
- Kadiri
- Kadthal
- Kaghaz Nagar
- Kaimur Bhabua
- Kaithal
- Kakinada
- Kalahandi
- Kalipahari
- Kallakurichi
- Kalligudi
- Kalyani
- Kamrup
- Kanadukathan
- Kanchipuram
- Kandhamal
- Kandukur
- Kangra
- Kanker
- Kannauj
- Kannur
- Kanpur
- Kanpur Dehat
- Kanpur Nagar
- Kansapuram
- Kanyakumari
- Kapurthala
- Karad
- Karaikal
- Karaikudi
- Karatholuvu
- Karauli
- Karbi Anglong
- Kargil
- Karimganj
- Karimnagar
- Karnal
- Karupatti
- Karur
- Karwar
- Kasaragod
- Kathua
- Katihar
- Katni
- Kattupakkam
- Kaushambi
- Kavaratti
- Kawardha
- Kendrapara
- Kendujhar
- Khagaria
- Khammam
- Khandwa
- Khanna
- Kharagpur
- Khargone
- Kheda
- Kheri
- Khorda
- Kichha
- Kinnaur
- Kiphire
- Kishanganj
- Kochi
- Kodagu
- Kodaikanal Observatory
- Koderma
- Kohima
- Kokrajhar
- Kolar
- Kolasib
- Kolhapur
- Kolkata
- Kollam
- Kooram
- Koppal
- Koraput
- Korba
- Koriya
- Kota
- Kothakudi
- Kothur
- Kottayam
- Kovilpatti
- Koyilandy
- Kozhikode
- Krishna
- Krishnagiri
- Kulgam
- Kullu
- Kumbakonam
- Kumburvayal
- Kundli
- Kupwara
- Kurnool
- Kurukkalpatti
- Kurukshetra
- Kurung Kumey
- Kushinagar
- Kutch
- Laddivadi
- Lahul & Spiti
- Lakhimpur
- Lakhisarai
- Lakshadweep
- Lalitpur
- Lambakheda
- Latehar
- Latur
- Lawngtlai
- Leh
- Lohardaga
- Lohit
- Lonavala
- Longleng
- Lower Dibang Valley
- Lower Subansiri
- Lucknow
- Ludhiana
- Lunglei
- Machur
- Madhepura
- Madhubani
- Madhupur
- Madikeri
- Madurai
- Mahabubabad
- Mahabubnagar
- Mahadanapuram
- Maharajganj
- Mahasamund
- Mahbub Nagar
- Mahe
- Mahendragarh
- Mahoba
- Mainaguri
- Mainpuri
- Majuli
- Malappuram
- Malda
- Malkangiri
- Malout
- Mammit
- Manakudi
- Manapparai
- Manawar
- Mandi
- Mandi Gobindgarh
- Mandla
- Mandsaur
- Mandya
- Mangalore
- Manipal
- Mannargudi
- Mansa
- Margao
- Marigaon
- Mathura
- Mau
- Mayurbhanj
- Medak
- Meenkashipuram
- Meerut
- Mehsana
- Melaparuthigudi
- Melpallam
- Melpattamkarisalkulam
- Melvisharam
- Midnapore
- Mirzapur
- Moga
- Mohali
- Mohanur
- Mokokchung
- Mon
- Moradabad
- Morena
- Muchipara
- Mughal Sarai
- Muktsar
- Mumbai
- Mumbai Extension
- Munger
- Murshidabad
- Muzaffarnagar
- Muzaffarpur
- Mysore
- Nabarangapur
- Nadia
- Nadiad
- Naduvakurichi
- Nagaon
- Nagapattinam
- Nagaur
- Nagpur
- Naidupuram
- Nainital
- Najibabad
- Nalanda
- Nalbari
- Nalgonda
- Namakkal
- Nanded
- Nandurbar
- Narayanpur
- Narmada
- Narnaul
- Narsinghpur
- Narsipatnam
- Nashik
- Navi Mumbai
- Navsari
- Nawada
- Nawanshahr
- Naxalbari
- Nayagarh
- Neemrana
- Neemuch
- Nelamangala
- Nellore
- Nerur
- New Delhi
- Nicobar
- Nilgiri
- Nilgiris
- Nizamabad
- Noida
- North 24 Parganas
- North And Middle Andaman
- North Cachar Hills
- North Dinajpur
- North Goa
- North Sikkim
- North Tripura
- Nowda
- Nuapada
- Nuh
- Nuvem
- Ooty
- Osmanabad
- Pakur
- Palakkad
- Palamalai
- Palamu
- Palani
- Palghar
- Pali
- Pambakovil Shandy
- Panaji
- Panchkula
- Panchmahal
- Panipat
- Panna
- Panvel - Station
- Papanasam
- Pappankulam
- Pappinaickenpatti
- Papum Pare
- Paradip
- Parbhani
- Pasumpon
- Patan
- Pathanamthitta
- Pathankot
- Patiala
- Patna
- Pauri Garhwal
- Pavitram
- Perambalur
- Peren
- Phalghat
- Phek
- Pilani
- Pilibhit
- Pinnathur
- Pithoragarh
- Pondicherry
- Ponga
- Poonamalle
- Poonch
- Porbandar
- Port Blair
- Prakasam
- Pratapgarh
- Proddatur
- Pudukkottai
- Pulankurichi
- Pulavadi
- Puludipatti
- Pulwama
- Pune
- Pungamuthur
- Purba Bardhaman
- Purbasthali
- Puri
- Purnia
- Puruliya
- Puzhal
- Quilon
- Raebareli
- Raichur
- Raigad Maharashtra
- Raigarh Chattisgarh
- Raikasba
- Raipur
- Raisen
- Rajahmundry
- Rajauri
- Rajgangpur
- Rajgarh
- Rajkot
- Rajnandgaon
- Rajpura
- Rajsamand
- Ramanagar
- Ramanathapuram
- Ramgarh
- Rampur
- Ranchi
- Rangareddi
- Rangareddy
- Ranipet
- Ratlam
- Ratnagiri
- Raurkela
- Rayagada
- Reasi
- Rewa
- Rewari
- Ri Bhoi
- Rishikesh
- Rohtak
- Rohtas
- Roorkee
- Ropar
- Rourkela
- Rudraprayag
- Rudrapur
- Rupnagar
- Rurka Kalan
- S.A.S. Nagar
- Sabarkantha
- Sagar
- Saharanpur
- Saharsa
- Sahibganj
- Saiha
- Salem
- Samastipur
- Sambalpur
- Sambhal
- Sangareddy
- Sangli
- Sangrur
- Sant Kabir Nagar
- Sant Ravidas Nagar
- Saran
- Satara
- Satna
- Sawai Madhopur
- Secunderabad
- Sehore
- Senapati
- Seoni
- Seraikela-Kharsawan
- Serchhip
- Shahapur
- Shaharanpur
- Shahdol
- Shahjahanpur
- Shahpura
- Shajapur
- Shamshabad
- Sheikhpura
- Sheohar
- Sheopur
- Shikohabad
- Shillong
- Shimla
- Shimoga
- Shivpuri
- Shrawasti
- Shyamnagar
- Sibmandir
- Sibsagar
- Siddharthnagar
- Sidhi
- Sihora
- Sikar
- Siliguri
- Silvassa
- Simdega
- Simga
- Sindhudurg
- Singrauli
- Sirkaali
- Sirmaur
- Sirohi
- Sirsa
- Sitamarhi
- Sitapur
- Sivaganga
- Sivakasi
- Sivasagar
- Siwan
- Solan
- Solapur
- Sonapur
- Sonarpur
- Sonbhadra
- Sonipat
- Sonitpur
- Soro
- South 24 Parganas
- South Andaman
- South Dinajpur
- South Garo Hills
- South Goa
- South Sikkim
- South Tripura
- Sricity
- Srikakulam
- Srinagar
- Subarnapur
- Sujangarh
- Sultanpur
- Sundergarh
- Supaul
- Surat
- Surendranagar
- Surguja
- T Pudupatti
- Tadipatri
- Talasari
- Tamenglong
- Tapi
- Tarn Taran
- Tawang
- Tehri Garhwal
- Tenkasi
- Thane
- Thanjavur
- The Dangs
- Theni
- Thimmarajanpettai
- Thirukkalukundram
- Thirukkannamangaikottam
- Thiruvaiyaru
- Thiruvarur
- Thoothukudi
- Thoubal
- Thrissur
- Thungavi
- Tikamgarh
- Timarni
- Tinsukia
- Tirap
- Tiruchendur
- Tiruchirappalli
- Tiruklalikundram
- Tirumani
- Tirunelveli
- Tirupati
- Tiruppur
- Tirupur
- Tirur
- Tiruttani
- Tiruvalla
- Tiruvallur
- Tiruvannamalai
- Tiruvarur
- Titilagarh
- Tohana
- Tonk
- Trimulgherry
- Trivandrum
- Tuensang
- Tumkur
- Turaiyur Koitpatti
- Tuticorin
- Udaipur Rajasthan
- Udaipur Tripura
- Udayarpalayam
- Udham Singh Nagar
- Udhampur
- Udupi
- Ujjain
- Ukhrul
- Umaria
- Una
- Unnao
- Upper Siang
- Upper Subansiri
- Uttara Kannada
- Uttarkashi
- Vadagarai
- Vadakara
- Vadodara
- Vaishali
- Valsad
- Vandavasi
- Vapi
- Varanasi
- Vattur
- Vellore
- Vidisha
- Vijayawada
- Vikarabad
- Villupuram
- Virudhunagar
- Visakhapatnam
- Visalakshi Nagar
- Vizianagaram
- Warangal
- Wardha
- Washim
- Wayanad
- West Champaran
- West Garo Hills
- West Godavari
- West Kameng
- West Khasi Hills
- West Midnapore
- West Nimar
- West Siang
- West Sikkim
- West Singhbhum
- West Tripura
- Wokha
- Y.S.R.
- Yadgir
- Yamunanagar
- Yavatmal
- Zunhebotto
Want to know more?
Read Our Editorial PolicyHave issue with the content?
Report Problem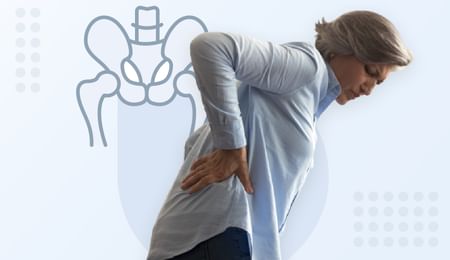
Osteoarthritis
Also known as Degenerative Joint Disease, Wear and Tear ArthritisOverview
Osteoarthritis is the most common joint disease that occurs due to age-related degenerative changes in the joints. Although it can affect any joints, the knees, spine, hips, and hands are the most affected.
It is the fourth leading cause of disability globally that affects 10-15% of all adults above the age of 60 years. It is the most common joint disease in India with a prevalence of 22-39%. Before the age of 45, osteoarthritis is more common in men, and as age advances, women are more predisposed to the condition.
It is characterized by breakdown of the cartilage (the tissue that cushions the ends of the bones between joints), bony changes of the joints, deterioration of tendons and ligaments, and various degrees of inflammation of the joint lining (called the synovium). Progressive pain, stiffness, and joint deformities are the primary symptoms of the disease.
Although there is no cure for the disease, medications, surgery, and alternative therapies can slow down disease progression and help patients lead comfortable and productive lives. Staying active, maintaining a healthy weight also helps in slowing the progression of the disease.
Key Facts
- Adults above 50 years of age
- Both men and women, but more common in women
- Knee joint
- Hip Joint
- Spine
- Hands
- Avascular Necrosis of Hip
- Bursitis
- Synovitis
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- Gout
- Ankylosing spondylitis
- NSAID analgesics: Ibuprofen, Diclofenac & Paracetamol
- Narcotics
- Muscle relaxants: Cyclobenzaprine
- Corticosteroids: Prednisolone
- Topical analgesics & sprays
- Medications for nerve pain
- Supplements
- Surgical management and other invasive procedures: Intra-articular injections, Alignment correction surgery & Joint replacement surgery
- Orthopaedic Surgeon
- Physiotherapist
Symptoms Of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is common as age advances. Individuals above the age of 60 have significant wear and tear in their joints, leading to the development of osteoarthritis. The following symptoms are commonly seen with osteoarthritis -
Knee Osteoarthritis
-
Chronic pain, tenderness, swelling in the knee joint
-
Reduced range of motion, stiffness in the knee joint
-
Crepitus or abnormal grinding sounds heard on joint movement
-
Bone spurs, which are extra bits of bone, which feel like hard lumps, can form around the affected joint.
-
Bone deformity
Hip Osteoarthritis
-
Chronic pain, tenderness, swelling in the hip joint
-
Reduced range of motion, stiffness in the hip joint
-
Crepitus or abnormal grinding sounds heard on joint movement
-
Joint deformity
Cervical Spondylosis (Osteoarthritis)
-
Pain and stiffness of the neck
-
Radiating or sharp shooting pain in the upper limbs
-
Tingling and/or numbness in the upper limbs
-
Dizziness
-
Vertigo
-
Grinding noise in the neck when the neck is turned sideways
Lumbar Spondylosis (Osteoarthritis)
-
Pain and stiffness of the lower back
-
Radiating or sharp shooting pain in the lower limbs and buttocks
-
Tingling and/or numbness in the lower limbs
-
Inability to stand or walk for longer durations
-
Balance problems
Causes Of Osteoarthritis
A lot of factors are responsible for osteoarthritis, such as:
Age-related degenerative changes
With increasing age, there is normal wear and tear of the joints, cartilages, ligaments, and other soft tissues in the body. These degenerative changes occur in various joints making them stiff. Degeneration of the joints also leads to formation of osteophytes which are extra bony protrusions and are characteristic to osteoarthritic joints. These can lead to immense pain and stiffness. In advanced stages, joint deformities occur that can severely impact function and mobility.
Heredity
Genetic factors likely influence the formation of osteophytes and degeneration of joints. This is likely attributed to polymorphism in genes regulating the inflammatory pathways. For example, Ehlers-Danlos syndrome, which is characterized by joint hypermobility, can contribute to osteoarthritis.
Environmental factors
A poor posture, lack of exercise, obesity, occupational hazards, such as lifting heavy weights, previous trauma to the joints cause faster wear and tear of the joints, leading to osteoarthritis.
Post menopause
Decreased estrogen as experienced by post-menopausal women increases the risk of knee osteoarthritis as estrogen is protective of bone health specifically reducing oxidative stress to the cartilage.
Risk Factors For Osteoarthritis
Certain risk factors may predispose an individual to develop osteoarthritis:
-
Age more than 50 years
-
Obesity/overweight
-
Diabetes
-
Elevated cholesterol levels
-
Hypothyroidism
-
Hyperparathyroidism
-
Acromegaly
-
Paget’s disease
-
Wilson disease
-
History of trauma to the joints
-
Faulty alignment of the joints
-
Occupational overuse of a joint. eg. athletes or people using hand drills
-
Improper weight-bearing
-
History of heavy weight lifting
-
Poor posture
-
Lack of exercise
Diagnosis Of Osteoarthritis
The following evaluations are performed by the doctor to confirm the diagnosis of osteoarthritis:
History and physical examination
The doctor will take a detailed history of the onset of symptoms, perform a thorough physical examination, and check for joint stiffness, muscle spasms, muscle strength, and neurological examination to evaluate the affected joints.
Imaging studies
-
X-Ray Both Knee Standing AP & Lateral Views - to study the bony changes in the knee joints.
-
MRI Both Knee Joints - to evaluate soft tissue changes around the knee joint.
-
X-Ray Hip Joint AP View - to study the bony changes in the hip joints.
-
MRI Both Hip Joint - to evaluate soft tissue changes around the hip joint.
-
X-Ray Cervical Spine AP & Lateral - to study the bony changes in the neck.
-
X-Ray Lumbar Spine AP & Lateral - to study the bony changes in the lower back.
-
MRI Screening of Whole Spine - to evaluate in detail the soft tissue and bony changes of the entire spine, such as disc desiccation, disc protrusion, ligament thickening, etc.
-
Bone Densitometry Whole Body - to check for concomitant osteoporosis, a condition where the bones lack calcium and become brittle and weak.
Other tests
-
Serum Calcium is advised to check for calcium deficiency that plays an important role in bone and joint pains.
-
Vitamin D (25 - OH) is to check for calcium deficiency that plays an important role in absorbing calcium in the body.
-
Although there's no blood test for osteoarthritis, certain tests can help rule out other causes of joint pain, such as rheumatoid arthritis.
-
Joint fluid analysis is a test in which your doctor might use a needle to draw fluid from an affected joint. The fluid is then tested for inflammation and to determine whether your pain is caused by gout or an infection other than osteoarthritis.
Celebs affected
Prevention Of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is an age-related condition that occurs due to unavoidable degenerative changes and wears and tears of the joints. A few things that can help prevent the occurrence of serious symptoms of osteoarthritis include:
-
Following a healthy diet rich in calcium and other minerals
-
Enough exposure to the morning sunlight to ensure a sufficient level of vitamin D in the body
-
Regular exercise to maintain strength and mobility in the joints
-
Following correct ergonomics while weight lifting and exercising
-
Avoiding sudden jerky and twisting movements of the joints
-
Avoiding squatting position and sitting cross-legged
Specialist To Visit
When symptoms of joint pain start to become bothersome, it is essential to visit an orthopedic doctor who will diagnose and treat the condition. Other doctors, such as neurologists, physiotherapists, help with the management of troublesome symptoms of osteoarthritis. The doctors to visit for osteoarthritis are -
-
Orthopedician - specialises in the diagnosis and treatment of disorders of the musculoskeletal system
-
Physiotherapist - for corrective exercises to increase strength and mobility in the joints and reduce pain
-
Neurologist - to manage the complications arising from osteoarthritis of the spine, such as tingling, numbness in the upper or lower limbs, weakness of upper or lower limbs, vertigo, headaches
-
Rheumatologist - for diagnosis and treatment of arthritis and other diseases of the joints, muscles, and bones
Treatment Of Osteoarthritis
The treatment of osteoarthritis mainly involves medical management & surgical management.
Medical Management
1. NSAID Analgesics: These include medicines like Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, and Paracetamol that help relieve pain and inflammation. These medicines must always be consumed with meals as taking them on an empty stomach can irritate the gastric lining.
2. Narcotics: This class of drugs may be required for more severe intensity pain, which is not relieved by the first line of medications. These tablets must be used only as prescribed by the physician as they are potentially habit-forming.
In 2010, the government (FDA) approved the use of duloxetine (Cymbalta) for chronic (long-term) musculoskeletal pain including from OA. This oral drug is not new. It also is in use for other health concerns, such as mood disorders, nerve pain and fibromyalgia.
3. Muscle relaxants: These drugs help relieve the painful spasms and stiffness associated with osteoarthritis of the spine. One of the most commonly used drugs in this category is Cyclobenzaprine.
4. Corticosteroids: This class includes medicine like Prednisolone which may be prescribed for a short duration or even as an injection to help resist pain. Joint injections with corticosteroids (sometimes called cortisone shots) or with a form of lubricant called hyaluronic acid can give months of pain relief from OA. This lubricant is given in the knee, and these shots may help delay the need for a knee replacement by a few years in some patients.
5. Topical analgesics & sprays: Topical application of analgesic ointments and sprays can help with symptomatic pain relief.
6. Medications for nerve pain: These are useful in providing relief from complications of osteoarthritis of the spine, such as radiating pain, tingling, numbness in the upper and lower limbs.
7. Supplements: Many over-the-counter nutrition supplements have been used for osteoarthritis treatment. Most lack good research data to support their effectiveness and safety. Among the most widely used are calcium, vitamin D and omega-3 fatty acids. Fish oils are also known to have anti- inflammatory properties. However, their use has been established mainly in rheumatoid arthritis. To ensure safety and avoid drug interactions, consult your doctor or pharmacist before using any of these supplements
Surgical Management and Other Invasive Procedures
Intra-articular Injections
In cases of severe pain that does not respond to medications, a Hydrocortisone injection may be given in the joint to offer quick relief. Hyaluronic Acid Injections are given in the joint to help with joint lubrication.
Alignment correction surgery
Corrective surgeries like osteotomy, laminectomy, spinal fusion are performed in severe joint deformities that cause limitation of function and pain.
Joint Replacement Surgery:
For severely damaged knees and hips, a prosthesis may be fitted, and the worn-out joints are completely replaced by mechanical joints. Though some of the joint changes are irreversible, most patients will not need joint replacement surgery.
At present, there is no treatment that can reverse the damage of OA in the joints. However, research is going on to find ways to slow or reverse this joint damage.
Transcutaneous electrical nerve stimulation (TENS):
This uses a low-voltage electrical current to relieve pain. It provides short-term relief for some people with knee and hip osteoarthritis.
Home Care For Osteoarthritis
Along with the medications, following home care tips can help manage symptoms and lead to the best possible disease outcomes:
-
Take a wholesome, balanced diet rich in calcium and other minerals.
-
Follow the exercise routine suggested by the doctor or physiotherapist.
-
Hot fomentation and application of topical analgesic preparations help relieve pain and stiffness.
-
Intermittent hot and cold treatments may provide temporary relief of pain and stiffness. Such treatments include a hot shower or bath and the careful application of heating or cooling pads or packs.
-
Gentle massage performed by a massage therapist can provide relaxation and promote pain relief.
-
Use joint supports, such as knee caps, cervical collar, lumbosacral belt to help support the spine.
-
Walking aids, such as a cane or walker, may help offload the diseased joints and promote safer walking and offer pain relief.
-
Avoid lifting heavyweights, and if done as a part of an exercise program, it must be done with extreme caution and correct ergonomic posture.
-
Change the mattress and sleeping pillow if not proper, and use the ones that offer good support and stabilize the spine.
-
Properly position and support your neck and back while sitting or sleeping.
-
Adjust furniture such as raising a chair or adjust your toilet seat to prevent pressure on the joints.
-
Avoid repeated motions of the joint, especially frequent bending.
Complications Of Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis is a disease that progresses with age. If enough care is not taken during the early stages of osteoarthritis, the following complications can occur:
-
A complete loss of mobility and extreme stiffness in the joints, rendering a patient bedridden or with severe walking issues.
-
Chronic debilitating pain that may interfere with sleep and be a source of anxiety or depression.
-
Neurological complications, such as paralysis, nerve pain, may occur as a result of advanced spondylosis.
Alternative Therapies Of Osteoarthritis
Along with medicines and topical analgesic preparations, various other treatment options help in the management of osteoarthritis:
Exercise and Yoga
Regular exercises and yoga focused on strengthening the joints and surrounding musculature and improving mobility are very helpful in managing the pain and stiffness caused by osteoarthritis.
Massage
A gentle massage improves blood flow in the affected parts, promotes relaxation, and helps with pain relief. Massages must be performed only by a qualified massage therapist.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapeutic modalities, such as Interferential Therapy (IFT) and Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation (TENS), are very useful in offering pain relief even from nerve pain. The rehabilitation exercises focus on strengthening and correcting weight-bearing of the joint and surrounding muscles, improving the overall strength and mobility of the affected joints.
Acupressure and Acupuncture
Chronic joint pain may respond to acupuncture or acupressure therapy, an alternative form of therapy that works by applying pressure or noxious stimuli on the peripheral trigger points.
Ayurveda
There are various Ayurvedic preparations in the form of oils and liniments. These are usually applied locally at the site of pain. They provide good relief from symptoms and promote joint health. Click here to know more about Ayurvedic remedies for knee pain.
Homeopathy
Homeopathic preparations in the form of injections or oral drops/pills, such as Rhus Toxicodendron, Arnica Montana, Solanum Dulcamara, etc., are known to improve pain and other troublesome symptoms of patients with osteoarthritis.
External Orthoses Support
Using knee caps, cervical collars, lumbosacral belts, and walking aids like a stick or walker offer much-needed support to the degenerative joints and are useful in alleviating pain due to osteoarthritis.
Living With Osteoarthritis
Osteoarthritis has a great impact on an individual’s quality of life. Severe, chronic, and debilitating pain may interfere with basic activities, such as walking, leading to restrictions in movements and travel. Often, chronic pain is a source of anxiety and depression in osteoarthritic patients, and they find themselves withdrawn from society and the community at large. Joining knee care and spine care clubs may help these patients deal with the degenerative changes and bond with others suffering similar pain.
Here are a few lifestyle changes one can incorporate into their routine life to ease off joint pains, especially during winter.
1. Supplement bone & joint healthy foods
-
Stock up dairy products and spend at least 15 minutes in sunlight daily to increase the intake of vitamin D.
-
Include foods rich in omega-3 fats such as salmon, nuts, fish oil in your diet as these ease inflammation.
-
Foods rich in vitamin K are helpful because of its pain-soothing properties. Include greens in your meal such as spinach, fenugreek (methi), cabbage, kale, etc.
-
Foods rich in vitamin C halt cartilage loss associated with arthritis. Add juicy oranges, sweet red peppers, tomatoes, amla and other vitamin C-rich foods in your diet.
2. Exercise regularly
Go for a 30-minute walk daily. If cold weather makes you lazy to go out in the mornings, go for an afternoon walk. Also, stretch your muscles as it helps maintain your mobility.
3. Stay hydrated
Drink plenty of water in winters as dehydration reduces flexibility and increases stiffness.
4. Get a massage
Massage therapy by a professional helps in relaxing the muscles around the painful joints, thereby reducing pain and making you more mobile.
5. Cover Up
Try to keep painful joints covered with a sleeve or wrap. Keeping them warm helps reduce pain and increases mobility. Using a muscle relaxant gel on the aching joints and then covering up has been seen to be very helpful.
6. Use hot packs/ice packs
Hot packs/hot baths/steam helps to soothe the painful joints. Heat stimulates blood flow, which brings healing nutrients to the affected area and inhibits the pain messages being sent to the brain.
7. Take medication on time
Do not forget to take your medications as advised by your doctor. If you suffer from chronic joint pain, consult your doctor for painkillers. Do not self-medicate. Also, go for regular doctor consultation, especially if your symptoms recur/worsen.
Looking for some simple yet effective exercises for knee pain? If yes, then watch this video to know expert-approved exercises and tips.
Frequently Asked Questions
Is osteoarthritis reversible?

How can I quickly relieve joint pain due to osteoarthritis?

Should I use a heat pack or ice pack for my painful joints?

How to select the correct size of a knee or spine brace?
References
- Osteoarthritis (OA). Centres for Disease Control and Prevention.
- Osteoarthritis. National Institute on Aging. U.S. Department of Health and Human Services.
- Priority Medicines for Europe and the World 2013 Update.
- The Epidemiology of Osteoarthritis in Asia. Marlene Fransen et al. Int J Rheum Dis 2011 May;14(2):113-21. doi: 10.1111/j.1756-185X.2011.01608.x.
- Long L, Ernst E. Homoeopathic remedies for the treatment of osteoarthritis: a systematic review. Database of Abstracts of Reviews of Effects (DARE): Quality-assessed Reviews [Internet]. York (UK): Centre for Reviews and Dissemination (UK); 1995.
- Osteoarthritis. National Health Portal of India.
- Cui A, Li H, Wang D, Zhong J, Chen Y, Lu H. Global, regional prevalence, incidence and risk factors of knee osteoarthritis in population-based studies. EClinicalMedicine. 2020;29-30:100587.